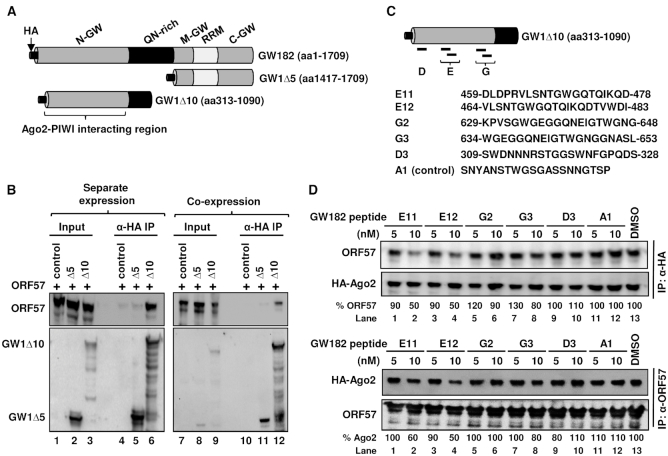
Figure 7.
ORF57 interacts with the N-terminal GW-rich domain (N-GW) of GW182 to disrupt GW182 interaction with Ago2. (A) Schematic diagram (not in scale) of GW182 (TNRC6A-2, 1709-aa) domains and two GW182 deletion mutants. (B) Mapping of ORF57–GW182 interacting domains. Total cell extract from HEK293T cells transfected with a vector expressing the HA-tagged N-terminal half of GW182 (GW1Δ10) or the C-terminal half of GW182 (GW1Δ5) or an empty vector (control) was mixed with the cell extract containing Flag-tagged ORF57 (B, left panel). Alternatively, Flag-tagged ORF57 was co-expressed in HEK293T cells with HA-tagged GW1Δ10, GW1Δ5, or an empty vector as a control (B, right panel). The cell extracts were then digested with RNase A/T1 before immunoprecipitation with an anti-HA antibody. The proteins pulled down by the co-IP were blotted for GW182-associated ORF57 by an anti-ORF57 antibody or by an anti-HA antibody for GW182. (C) Schematic illustration (not in scale) of ORF57-interacting GW1Δ10 (aa 313-1090) and its derived peptides previously shown to bind Ago2. The sequence and deduced position of each peptide (E11, E12, G2, G3 and D3) in GW182 are originated from a reported study on TNRC6B-1 (1723-aa) (44). A control peptide (A1) not binding to Ago2 (44) served as a control. (D) GW182-derived peptide competitive binding assays. HA-tagged Ago2 from HEK293T cells was immobilized on anti-HA antibody-coated beads (top panel). The HEK293T cell extract containing ORF57 was pre-mixed with individual GW182 peptides for 2 h at room temperature. This mixture was then added to the Ago2-immobilized beads and was incubated overnight at 4°C. The ORF57 protein associated with HA-ago2 beads in the pulldown assays was blotted by using an anti-ORF57 antibody and an anti-HA antibody for the constant Ago2 level (top panel). The binding of ORF57 (%) to HA-Ago2 in the presence of a GW182 peptide was measured based on the band intensity after normalized to the ORF57 level bound to HA-Ago2 in the presence of DMSO, which set as 100%. Alternatively, ORF57 from HEK293T cells was immobilized on polyclonal anti-ORF57 antibody-coated beads (lower panel). HA-Ago2 expressed in HEK293T cells was pre-mixed with the individual GW182 peptides for 2 h at room temperature. The mixture was then added to the ORF57-immobilized beads and incubated overnight at 4°C. The HA-Ago2 protein associated with ORF57 in the presence of GW182 peptides in the pulldown assays was blotted using an anti-HA antibody and the constant ORF57 level in each sample was blotted with anti-ORF57 antibody for the pulldown efficiency (lower panel). The binding of HA-Ago2 (%) to ORF57 in the presence of a GW182 peptide was measured as described above.