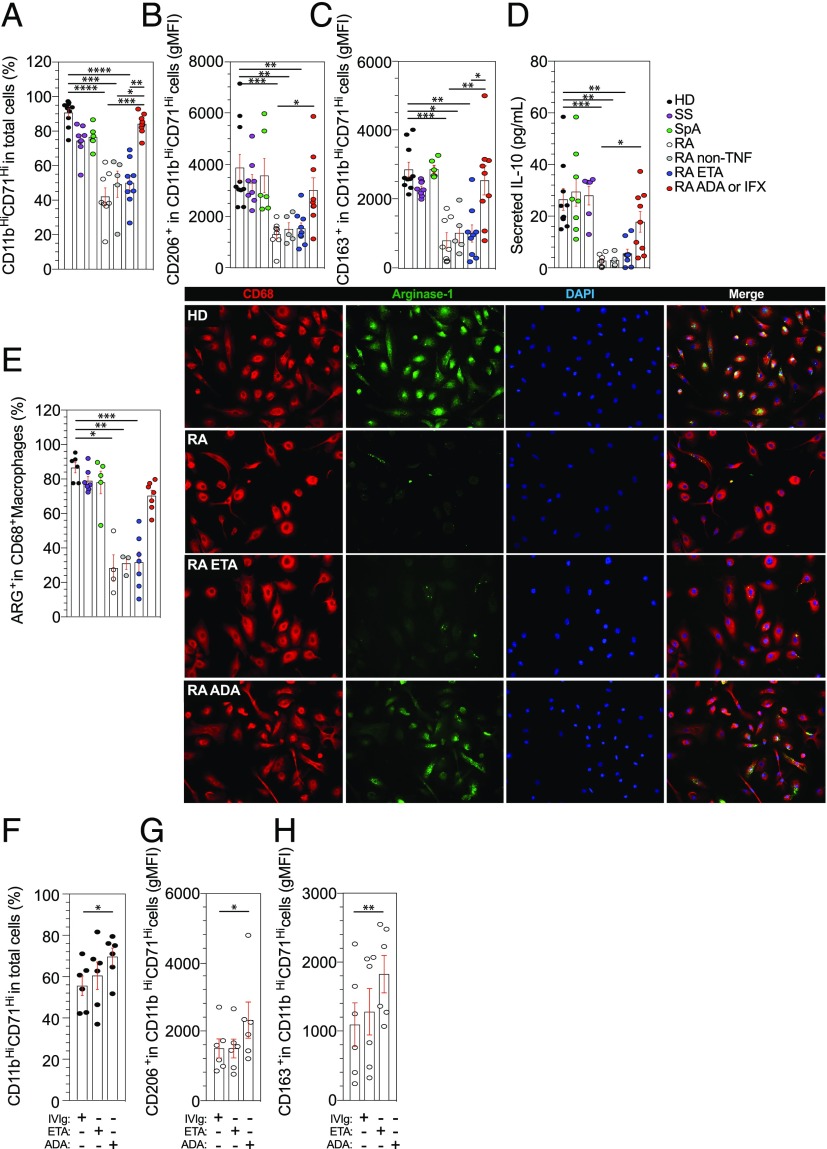
FIGURE 3.
A specific defect in M2-like polarization of RA monocytes as compared with SS and SpA patients. (A–C) The differentiation of blood monocytes into M2-like macrophages by SAB was assessed in HD (n = 10) and in patients with SS (n = 8), SpA (n = 6), RA treated with MTX (n = 8), RA treated with MTX + ETA (n = 9), and RA treated with MTX + ADA or IFX (n = 9) and RA treated with MTX + non-TNFi biologic (n = 5) by flow cytometry analysis using anti-CD11b and anti-CD71 Abs (A). Specifics markers of M2-like macrophages polarization were assessed, CD206 (B) and CD163 (C). (D) Concentrations of IL-10 in cell culture supernatant were detected by ELISA after 6 d. (E) Representative images and frequencies of CD68+ Arg+ detected in HD (n = 6) and in patients with SS (n = 7), SpA (n = 5), RA treated with MTX (n = 4), RA treated with MTX + ETA (n = 7), and RA treated with MTX + ADA or IFX (n = 7) and RA treated with MTX + non-TNFi biologic (n = 3). Scale bar, 10 μm. (F–H) TNFi or control treated purified monocytes were harvested after 6 d in macrophage SAB medium and analyzed for M2-like polarization with anti-CD11b, anti-CD71, anti-CD206, anti-CD163, and live-death (HD n = 6 and RA n = 6 [four were on MTX, one on rituximab, and one on tocilizimab]). Results are shown as mean ± SEM. Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn multiple comparisons *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001.