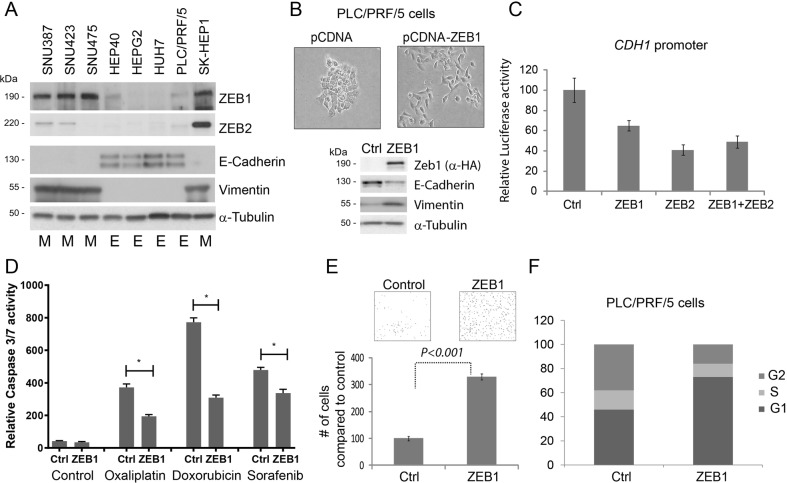
Fig. 2. Transcription factors of ZEB family are expressed in HCC-derived cell lines and contribute to epithelial plasticity.
a Expression of ZEB1, ZEB2, E-Cadherin and vimentin proteins was assessed by western blotting in eight Hepatoma-derived cell lines. Cell lines identified as epithelial are marked with “E”, mesenchymal with “M”. b Transient expression of ZEB1 induced cell scattering and affected canonical markers of EMT in PLC/PRF/5 cells such as increased vimentin and decreased E-Cadherin protein expression. c Both ZEB1 and ZEB2 suppressed CDH1 promoter in transient reporter assay. d ZEB1-induced EMT facilitates resistance to apoptosis to commonly used chemotherapeutic agents used in HCC treatment. Cells were treated with 100 μM Oxaliplatin (Ox), 2 μg/ml Doxorubicin (Dox) and 10 μM Sorafenib (Sor) for 24 h. Arbitrary units of luciferase activity defining apoptosis (caspase 3/7 activity) has been presented. In all cases, ZEB1-expressing cells became resistant to cell death. (*) is p < 0.05 as assessed by Student’s t-test. e ZEB1-induced EMT facilitates cell motility as assessed by transwell-migration assay. PLC/PRF/5 cells expressing ZEB1 are significantly (approximately three times) more motile compared with control. f Assessment of cell cycle profile 3 days after ZEB1 overexpression revealed an enrichment of G1 cells indicating cell cycle arrest