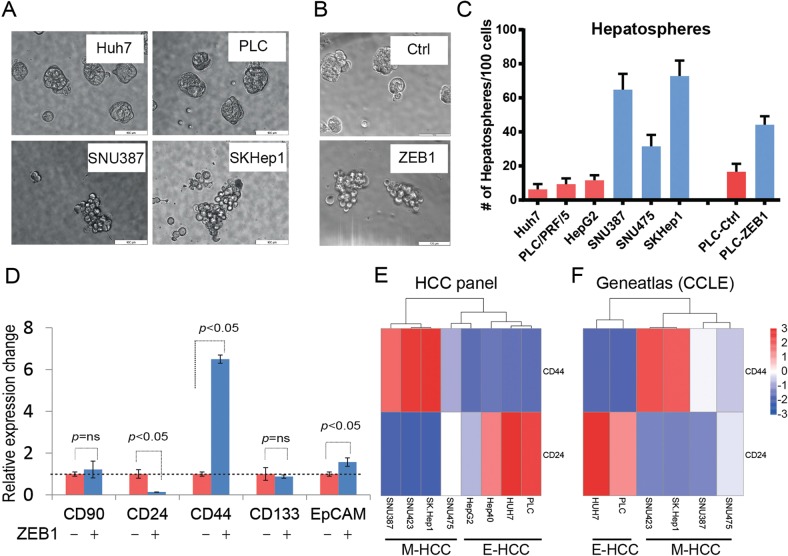
Fig. 4. M-HCC phenotype is associated with enhanced hepatosphere formation and CD44high/CD24low profile.
a In conditions of non-adherent growth, E-HCC cells produced spherical and smooth hepatospheres (top panels). M-HCC cells (bottom panels) produced loosely attached cell clusters in the shape of a grape bunch. b ZEB1-induced EMT mimics the phenotype observed in M-HCC cells. c E-HCC and M-HCC cells show stark differences in terms of number of hepatospheres formed. M-HCC cells or EMT phenotype induced by ZEB1 increases the number of hepatospheres formed indicating they contain more stem cell-like cells. d A panel of currently used stem cell markers were assessed by qPCR in HCC upon ZEB1 overexpression. The changes in CD44, EpCAM and CD24 were significant. Among the changing ones CD44 (increase) CD24 (decrease) were most prominent. The analysis of CD44 and CD24 in E- and M-HCC cells by qPCR (e) or RNA-seq by probing geneatlas database (f). The expression data in the form of ΔΔcT (e) or “reads” (f) were presented after non-hierarchical cluster analysis. E- and M-HCC cells clustered as a result of CD24 and CD44 expression