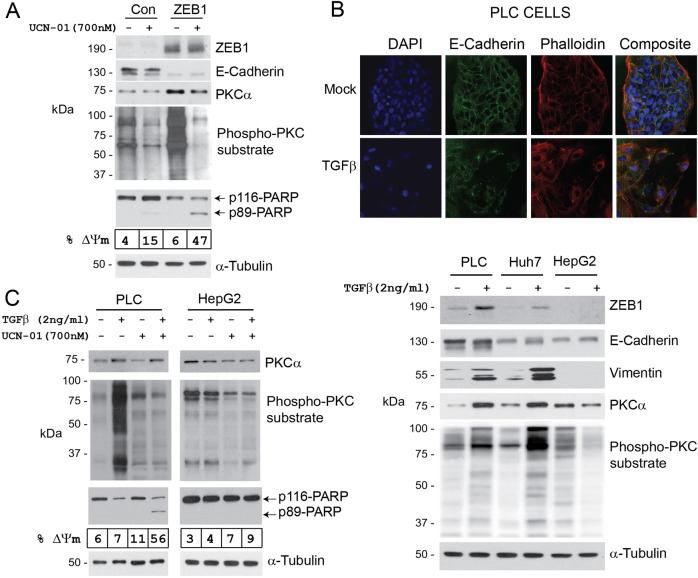
Fig. 7. ZEB1- or TGFβ-induced EMT renders E-HCC cells sensitive to UCN-01.
a PLC/PRF/5 cells were transfected with pCDNA4 (Con) or pCDNA4-ZEB1 (ZEB1) plasmids. Seventy two hours later and after hallmarks of EMT were observed, cells were treated with 700 nM UCN-01 for 8 h. UCN-01 treatment resulted in significant (47%) apoptosis in ZEB1-expressing cells compared with the control (15%) as assessed by PARP cleavage and mitochondria depolarization. PKCα protein abundance and PKC activity were increased as a result of ZEB1-induced EMT. b Three E-HCC cell lines were treated with TGFβ (2 ng/ml) for 72 h. EMT was confirmed by the analysis of cell morphology, E-Cadherin and vimentin protein expression and localization. All E-HCC cells, with the exception of HepG2, responded to TGFβ showing increased ZEB1 and vimentin expression, cytoplasmic re-distribution of E-Cadherin, disappearance of cortical actin (phalloidin staining) and cell scattering. PKCα abundance and activity were also increased as a result of TGFβ-induced EMT. c TGFβ-responsive (PLC/PRF/5) and non-responsive (HepG2) cells were incubated with TGFβ for 72 h and treated with 700 nM UCN-01 for an additional 8 h. PKC abundance and activity were assessed by western blotting along with the pro-apoptotic activity of UCN-01 as detected using flow cytometry (mitochondria depolarization, % ΔΨm) and PARP cleavage. TGFβ treatment rendered PLC/PRF/5, but not HepG2, cells sensitive to UCN-01-induced cell death