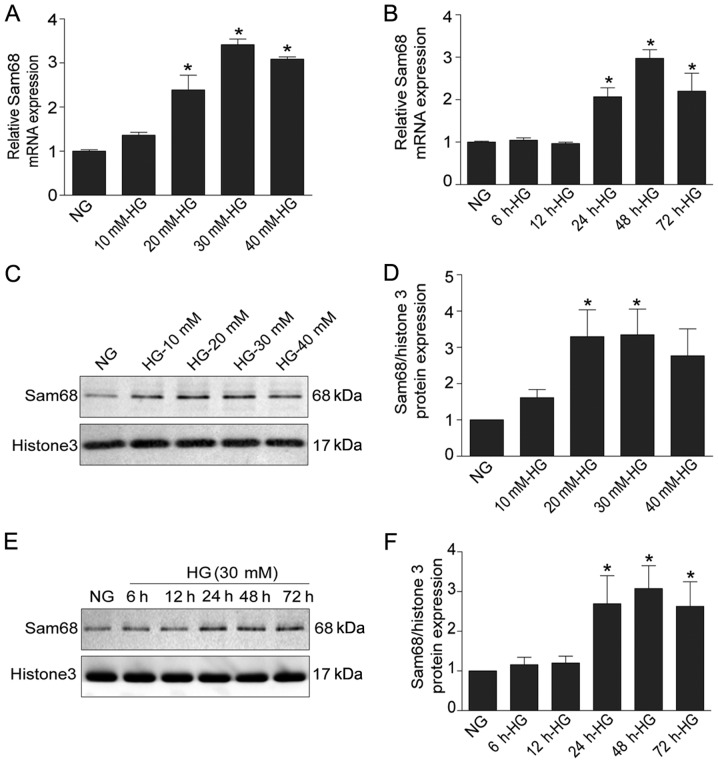
Figure 1.
Sam68 is increased in HG-treated podocytes in vitro. (A) The effects of HG with different concentrations on the mRNA expression of Sam68. (B) The effects of HG at different time-points on the mRNA expression of Sam68. The mRNA level of Sam68 was detected using real-time-quantitative PCR, and was calculated with the 2−ΔΔCq method. (C) The protein level of Sam68 was detected by immunoblotting in the nuclear extract of podocytes treated with different concentrations of glucose. Histone H3 was used as a nuclear protein loading control. (D) Densitometric analysis of three independent experiments displayed in C. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. *P<0.05 HG (20 mM, 30 mM, 40 mM) vs. NG. (E) The protein expression of Sam68 was detected by immunoblotting in the nuclear extract of podocytes incubated with HG at different time-points. Histone H3 was used as the nuclear protein loading control. (F) Densitometric analysis of three repetitions of the experiment displayed in E. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. *P<0.05, 24 HG (30 mM) or 48 h HG (30 mM) or 72 h HG (30 mM) vs. NG. Sam68, Src-associated substrate during mitosis of 68 kDa; HG, high glucose; PCR, polymerase chain reaction.