Figure 2.
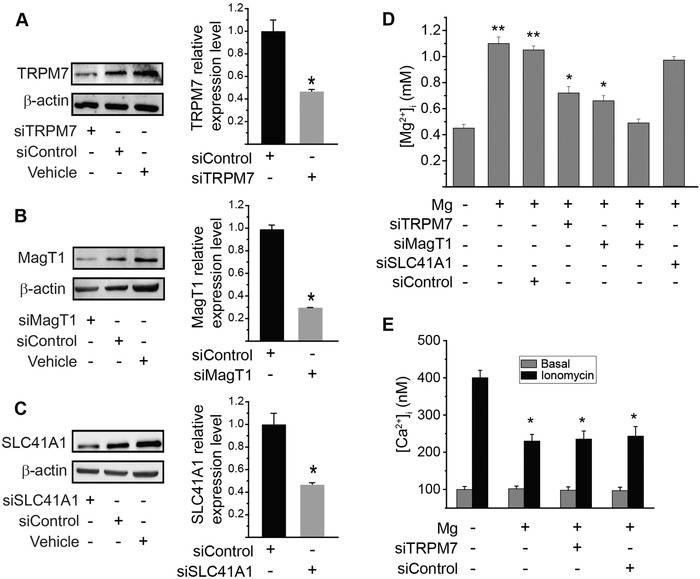
Intracellular Mg2+ concentration and Ca2+ influx in endothelium. A–C) siRNA knockdown of TRPM7, MagT1, and SLC41A1. Western blots showing expression of specific proteins in endothelial cells after treated with control siRNA or siRNA against TRPM7, MagT1, or SLC41A1; and quantitative measurements of relative protein levels from Western blots. (*P < 0.05, compared to control group; n = 4). D) Cells were transfected with siRNA against TRPM7, MagT1, SLC41A1, or scramble control siRNA, and were incubated with Mg2+‐free Ca2+‐containing medium for 15 min before being treated with high Mg2+ (2 mmol L−1 “+”) or Mg2+‐deficiency (0.1 mmol L−1 “–”). Mag fura‐2AM intensity was measured one minute after Mg2+ addition. (*P < 0.05, vs Mg2+‐deficiency or group treated with MagT1 siRNA and TRPM7 siRNA; **P < 0.01, vs Mg2+‐deficiency or group treated with MagT1 siRNA and TRPM7 siRNA; n = 3). E) Mg2+ inhibits Ca2+ influx in endothelium as an antagonist of Ca2+. Intracellular Ca2+ concentration measured by fura‐2AM intensity. Fura‐2AM intensity were recorded before ionomycin addition as basal level and one minute after ionomycin (10−6 mol L−1) addition. (* P < 0.05, vs Mg2+‐deficiency; n = 4).
