Figure 1.
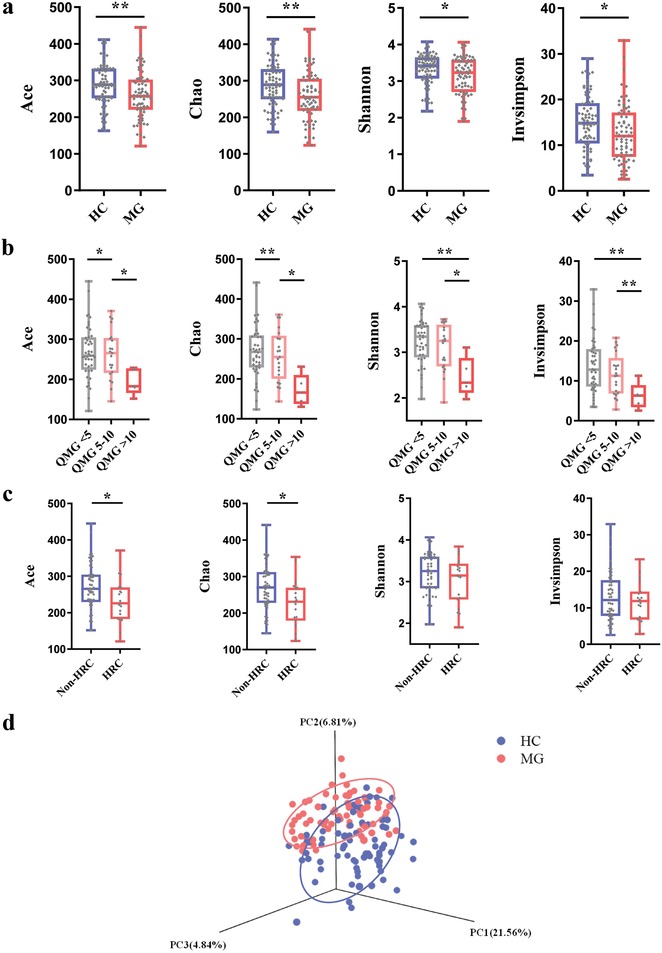
Gut microbial characteristics of myasthenia gravis (MG). a) α‐phylogenetic diversity analysis showing that MG subjects were characterized by lower microbial richness in four indexes (Ace, Chao, Shannon, and Invsimpson) relative to healthy controls (n = 74, HC; n = 70, MG). b) The MG subjects with different QMG scores showing different α‐phylogenetic diversity indexes (n = 70, MG). The four α‐ diversity indexes consistently decreased with the increases of QMG scores, highlighting a robust association between lower some α‐ diversity indexes and MG severity.(QMG < 5, n = 44; QMG = 5–10, n = 21; QMG > 10, n = 5). c) The MG subjects with history of respiratory crisis (HRC, n = 19) showing lower ACE and Chao indexes compared to the non‐history of respiratory crisis subjects (Non‐ HRC, n = 51). As the HRC is a hallmark of MG severity, this finding also confirms the association between α‐ diversity indexes and MG severity. d) At the operational taxonomic units (OTU) level, 3D principal co‐ordinates analysis showed that gut microbial composition of patients with MG was significantly different from that in healthy controls (n = 74, HC; n = 70, MG).
