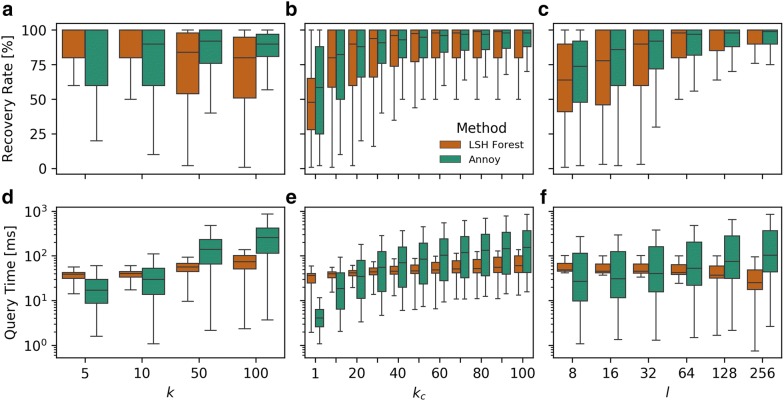
Fig. 8.
ChEMBL () k-nearest neighbor searches performance of 2048-D MHFP6 indexed using LSH Forest and 2048-D ECFP4 indexed using Annoy Recovery rates for both implementations depend on parameters , , and . a While LSH Forest performs better for and nearest neighbors, Annoy surpasses LSH Forest for and . b By increasing the number of nearest neighbors by a factor of , the performance of both ANN neighbor methods can be greatly improved. While LSH Forest (orange) shows worse performance compared to Annoy (green) for , it surpasses Annoy for higher values. c Increasing the number of trees increases the recovery rate for both methods at the expense of main memory. Annoy performs slightly better for , performance of LSH Forest increases at a greater rate, overtaking Annoy at . d, e Increasing values of parameters and affects query times of Annoy negatively. While the average query time for LSH Forest remains below 100 ms for and , Annoys average query time increases to above 100 and 200 ms respectively. f As the number of prefix trees, and thus the recovery rate, in LSH Forest increases, the query time decreases. On the other hand, an increase in Annoy trees, with a beneficial effect on recovery rate, also increases the query time. For subplots a, d; b, e; and c, f; the data has been aggregated over all measured values for , ; , ; and , ; respectively