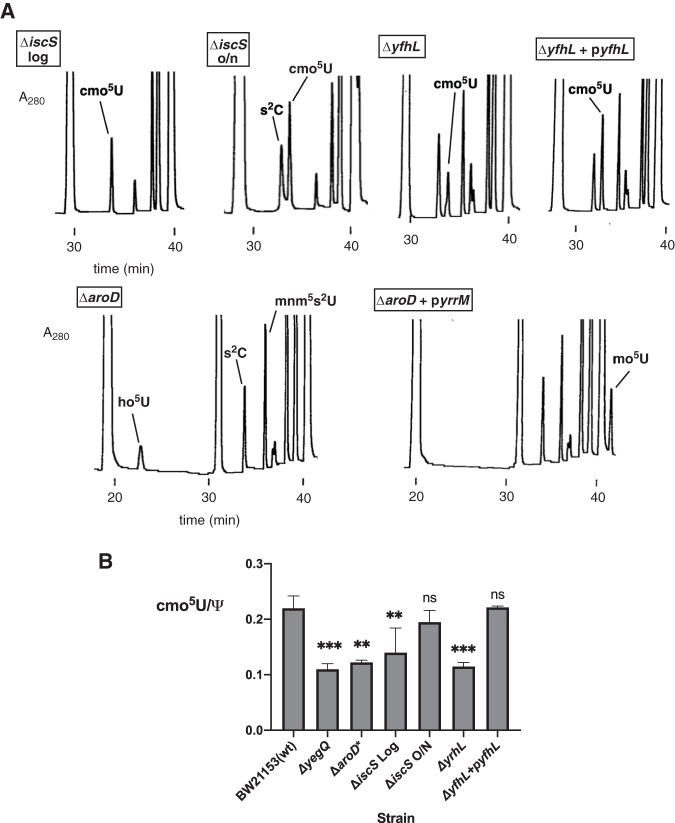
FIG 5.
Effects of other genes on xo5U levels. (A) HPLC analysis of iscS, yfhL, and aroD in E. coli. The iscS mutant lacks thionucleosides s2C and mnm5s2U and cmnm5s2U in this region but still retains cmo5U, which is decreased to a similar level as the yegQ mutant (shown in panel B). The overnight iscS mutant culture shows significant increases in s2C and some increase in cmo5U, similar to increases in other Fe-S-dependent modifications. The effect on cmo5U is not statistically significant due to variability in the log-phase data. An E. coli strain lacking the ferredoxin yfhL shows a similar HPLC spectrum as that of the yegQ mutant and a similar level of reduction in cmo5U (shown in panel B). In E. coli, shikimate pathway genes, such as aroD, are required for conversion of ho5U to cmo5U and for wt levels of ho5U, as previously reported (15, 19). Quantifying the level of ho5U shows the same reduction in ho5U as for cmo5U in the yegQ and yfhL mutants. (B) Quantitative analysis of HPLC data for E. coli aro, iscS, and yfhL mutants relative to those of the wt strain. *, the aroD strain lacks the ability to synthesize cmo5U from ho5U and thus the ratio reported here is for ho5U/Ψ. ***, P < 0.001 compared to wt (unpaired t test); **, P < 0.01 compared to wt; ns = no statistical significance among these strains or with the wt strain.