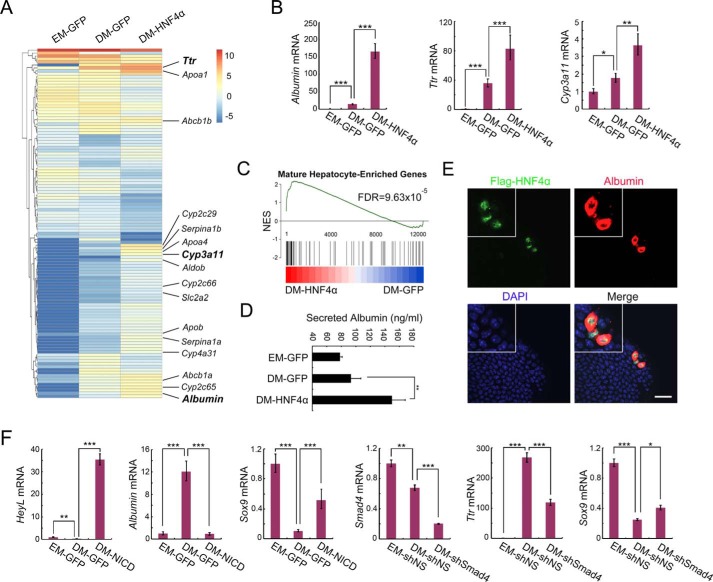
Figure 3.
AAV-DJ vector–mediated gene manipulation enables dissection of gene function in cholangiocyte-to-hepatocyte differentiation. A, liver ductal organoids were transduced with AAV-DJ–HNF4α or AAV-DJ–GFP and then subjected to hepatocyte differentiation induction. On day 5 of differentiation, organoids were collected for bulk RNA-Seq analysis. A clustered heatmap of log2-transformed reads per kilobase million shows differentially expressed genes. Hepatocyte marker genes are indicated on the right. EM, expansion medium. B, qRT-PCR validation of Albumin, Ttr, and Cyp3a11 expression in A. C, GSEA plot of DM-HNF4α and DM-GFP compared with a gene list containing the top 300 expressing genes in adult liver compared with embryonic liver. NES, normalized enrichment score. D, organoid culture medium was collected for an albumin ELISA assay to detect secreted albumin. E, organoids infected with low-dose AAV-DJ–HNF4α were subjected to differentiation. Confocal images show staining of FLAG-HNF4α (green), albumin (red), and DAPI (blue). Magnification, ×2. A representative result of three independent experiments is shown. Scale bar = 20 μm. F, organoids were transduced with AAV-DJ–NICD or AAV-DJ–shSmad4, subjected to differentiation, and then harvested to examine expression of the indicated genes using qRT-PCR. shNS, nonspecific shRNA; shSmad4, Smad4 shRNA. For qRT-PCR, histone H3 was used as an internal control. The statistical data represent mean ± S.D. (n = 3). ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05.