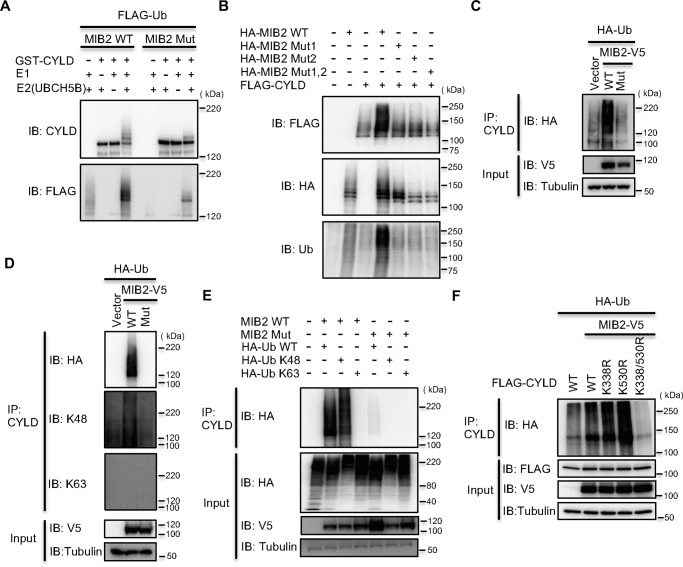
Figure 2.
MIB2 ubiquitinates CYLD via Lys-48–linked polyubiquitin chain. A, analysis of CYLD ubiquitination by MIB2 in vitro. In vitro ubiquitination assay was performed using recombinant GST-CYLD as a substrate in the presence of FLAG-tagged ubiquitin, E1 (UBE1), E2 (UbcH5B), recombinant His-tagged WT MIB2 (MIB2 WT) and catalytically inactive MIB2 (MIB2 Mut) in various combinations as indicated. B, identification of RING domains of MIB2 indispensable for CYLD ubiquitination. In vitro ubiquitination assay was performed using recombinant HA-tagged WT MIB2 (MIB2 WT), a MIB2 RING1 mutant (Mut1), a MIB2 RING2 mutant (Mut2), and a RING1/RING2 double mutant of MIB2 (Mut1, 2) in various combinations as indicated. C, analysis of CYLD ubiquitination by MIB2 in cell. MIB2 was expressed in HEK293T cells along with HA-ubiquitin. Ubiquitination of the endogenous CYLD was evaluated by immunoprecipitation of CYLD using an anti-CYLD antibody followed by anti-HA immunoblotting. Vector: mock pcDNA3.2, Mut: catalytically inactive form. D, identification of the type of polyubiquitination chain of MIB2 for CYLD ubiquitination using specific antibody. V5-tagged WT or catalytically inactive MIB2 (Mut) was expressed in HEK293T cells along with HA-tagged WT ubiquitin (Ub). Cells were treated with MG132 (10 μm) for 6 h and the level of CYLD ubiquitination was evaluated by immunoprecipitation of CYLD using an anti-CYLD antibody followed by immunoblotting with anti-HA, anti–Lys-48 (K48) Ub, or anti–Lys-63 (K63) Ub antibodies. E, determination of the type of polyubiquitination chain of MIB2 for CYLD ubiquitination using ubiquitin mutants. FLAG-tagged CYLD was co-transfected with either control, WT MIB2, or catalytically inactive MIB2 (Mut), along with either HA-tagged WT, Lys-48, or Lys-63 ubiquitin (Ub). Cells were treated with MG132 (10 μm) for 6 h and the level of CYLD ubiquitination was evaluated by immunoprecipitation of CYLD using an anti-CYLD antibody, followed by anti-HA immunoblotting. F, identification of CYLD-ubiquitination site by MIB2. WT MIB2 was expressed in HEK293T cells along with HA-ubiquitin and either WT CYLD or three CYLD mutants (K338R, K530R, and K338/530R). Ubiquitination of the overexpressed CYLD was evaluated by immunoprecipitation of CYLD using an anti-FLAG antibody followed by anti-HA immunoblotting.