Figure 1.
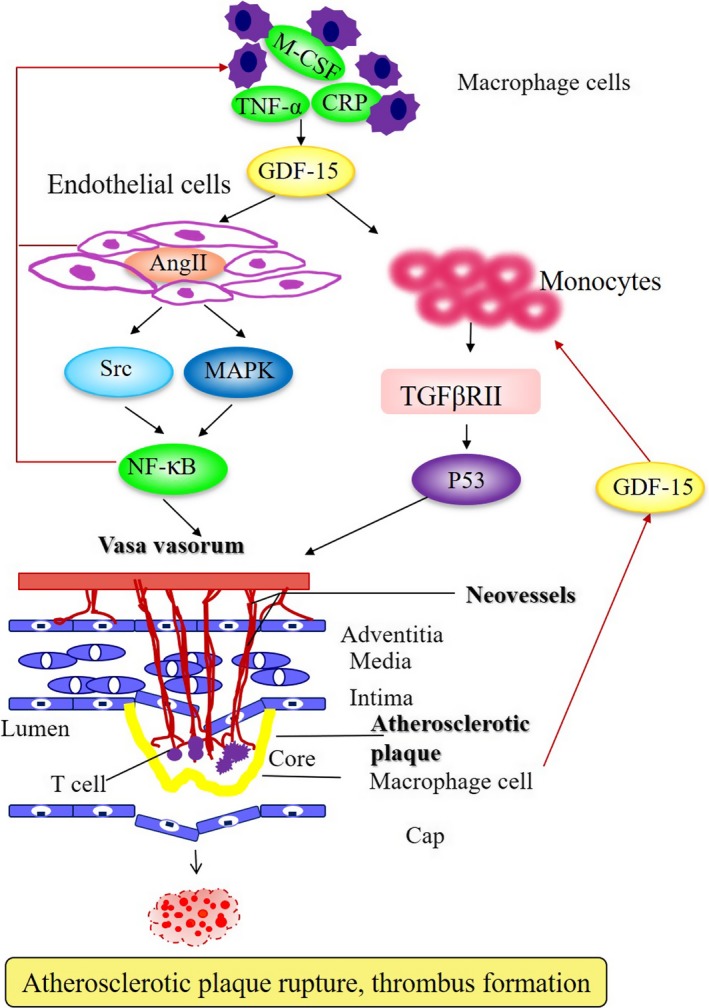
Schematic overview of a vulnerable plaque in advanced atherosclerosis. Plaque formation is initiated by endothelial cell dysfunction and subsequent angiogenesis and release of proinflammatory factors mediated by GDF‐15, contributing to the progression of atherosclerotic lesions and the development of plaque rupture and thrombus formation in atherosclerotic status. CRP indicates C‐reactive protein; GDF‐15, growth differentiation factor 15; MAPK, mitogen‐activated protein kinase; M‐CSF, macrophage colony‐stimulating factor; TGF‐βRII, transforming growth factor‐βRII; TNF‐α, tumor necrosis factor‐α.
