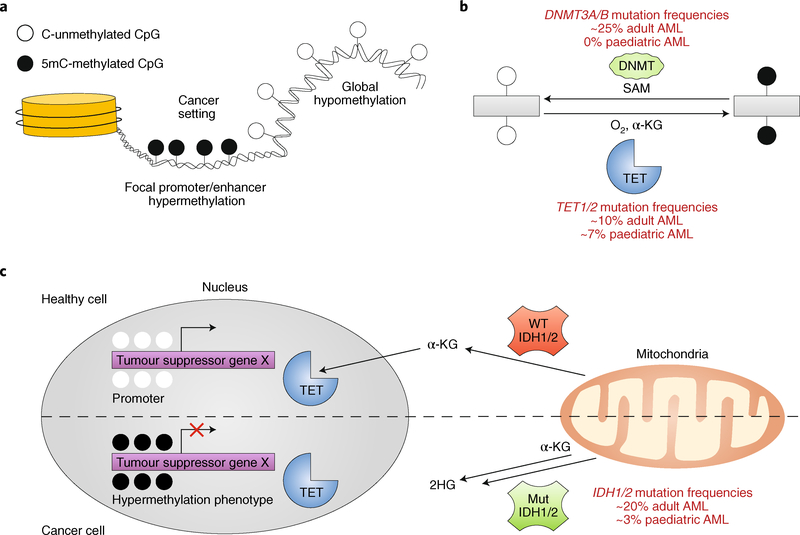
Fig. 2 |. DNMT and TET enzymes and related perturbations in AML.
a, Global hypomethylation and focal promoter/enhancer hypermethylation phenotypes are commonly detected in cancer. b, DNMT and TET enzymes are commonly mutated in adult AML and counteract one another via deposition or removal of the 5mC mark, respectively. DNMTs deposit a methyl group on to the carbon-5 position of cytosine using S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM) as a substrate, and TET enzymes rely on ɑ-ketoglutarate (ɑ-KG) and oxygen to oxidize 5mC and promote cytosine demethylation. c, IDH1/2 (encoding isocitrate dehydrogenase 1) mutations, which are common in AML, inhibit TET activity by converting the TET substrate ɑ-KG to 2-hydroxyglutarate (2HG), resulting in a hypermethylation phenotype. WT, wild type.