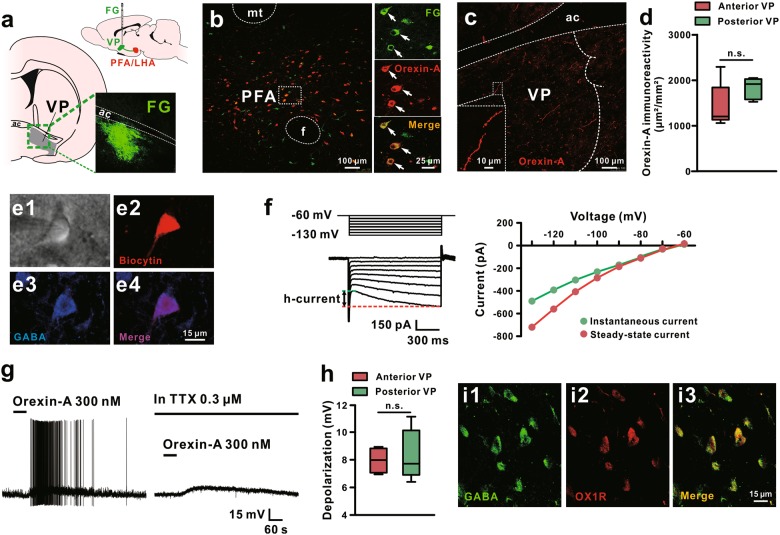
Fig. 2.
Orexinergic neurons in the hypothalamus directly project to VP and orexin depolarizes GABAergic VP neurons. a Diagram and a coronal brain section showing the identification of PFA/LHA-VP orexinergic projections with injections of FG into the VP. b Double immunoreactivity of orexin-A (red) and FG (green) in the same PFA/LHA neurons. c Orexinergic fibers in the VP and their varicosities. d Surface area of immunoreactivity for orexinergic fibers in the anterior and posterior VP of rats (n = 5). e, f Morphological, immunohistochemical, and electrophysiological identifications of the recorded GABAergic neurons in the VP. Based on infrared differential interference contrast images, VP neurons with diameters around 15 μm were patched as candidate GABAergic neurons (e1). Immunochemistry was used to identify GABAergic VP neurons by immunostaining the recorded biocytin-filled neurons with GABA (e2-e4). A series of 1 s hyperpolarizing voltage steps (ranging from −60 to −130 mV in 10 mV steps) were employed to observe inwardly rectifying h-currents, a feature of GABAergic VP neurons, in recorded neurons (f). g Orexin-A depolarized the recorded VP neurons and brought up the neurons firing. The orexin-induced depolarization on VP neurons did not blocked by TTX, suggesting a direct postsynaptic effect of orexin. h Group data of the tested VP neurons (n = 5 for anterior and posterior VP, respectively). i Double immunoreactivity of GABA (green) and OX1R (red) in the same VP neurons. mt mammillothalamic tract, aca anterior commissure, ant, PFA perifornical nucleus, VP ventral pallidum. Data are represented as median (horizontal bar) with 25th–75th (box) and 10th–90th (whiskers) percentiles; n.s. indicates not significant, by two tailed unpaired t-test (d, h)