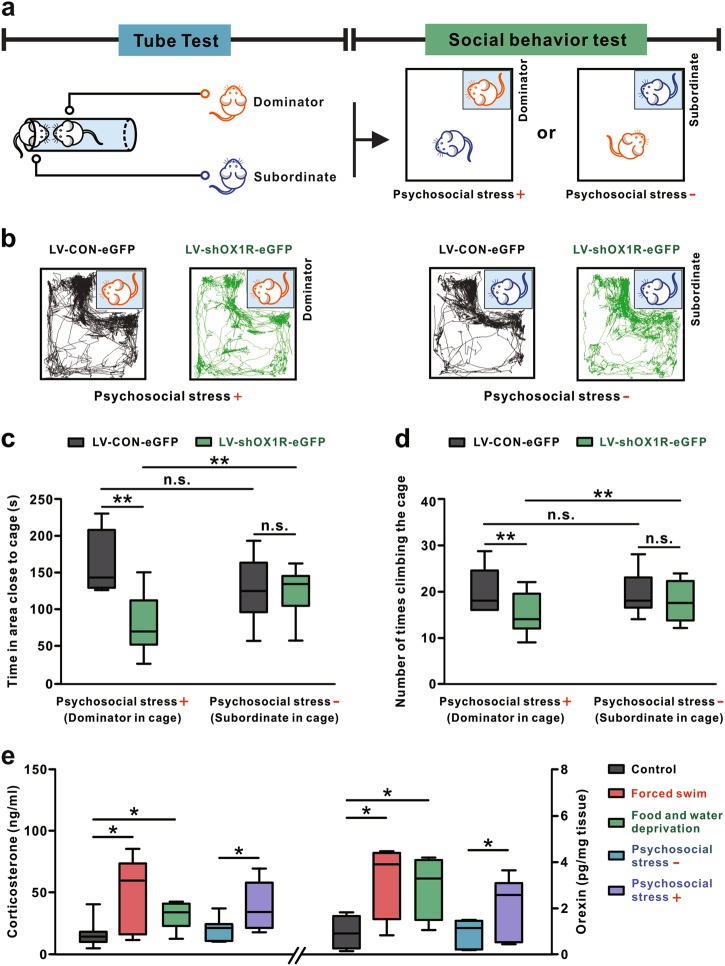
Fig. 5.
Endogenous orexin in VP alleviates social avoidance under acute psychosocial stress. a Scheme of experimental paradigm showing the social interaction tests, with or without psychosocial stress, between the pair of dominator and subordinate rat competed from an antecedent tube test. b Traces of rats treated with LV-shOX1R-eGFP or LV-CON-eGFP in the social interaction tests in the presence or absence of psychosocial stress. c Time that subordinate/dominator rats treated with LV-shOX1R-eGFP or LV-CON-eGFP spent in the area close to the caged dominator/subordinate (n = 9–10 per group). d Number of times of subordinate/dominator rats treated with LV-shOX1R-eGFP or LV-CON-eGFP climbing the cage in the presence and absence of psychosocial stress (n = 9–10 per group). n = 10 for the LV-CON-eGFP subordinate and LV-shOX1R-eGFP dominator group, and n = 9 for the LV-shOX1R-eGFP subordinate and LV-CON-eGFP dominator group. e ELISA analyses show serum corticosterone (n = 6–7 per group) and orexin-A level in VP (n = 12) under different stress and non-stress conditions. n = 6 for food/water deprivation group, and n = 7 for other groups. Data are represented as median (horizontal bar) with 25th–75th (box) and 10th–90th (whiskers) percentiles; n.s. indicates not significant and *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, by two-way (c, d) or one-way (e) ANOVA followed by Bonferroni-corrected t test