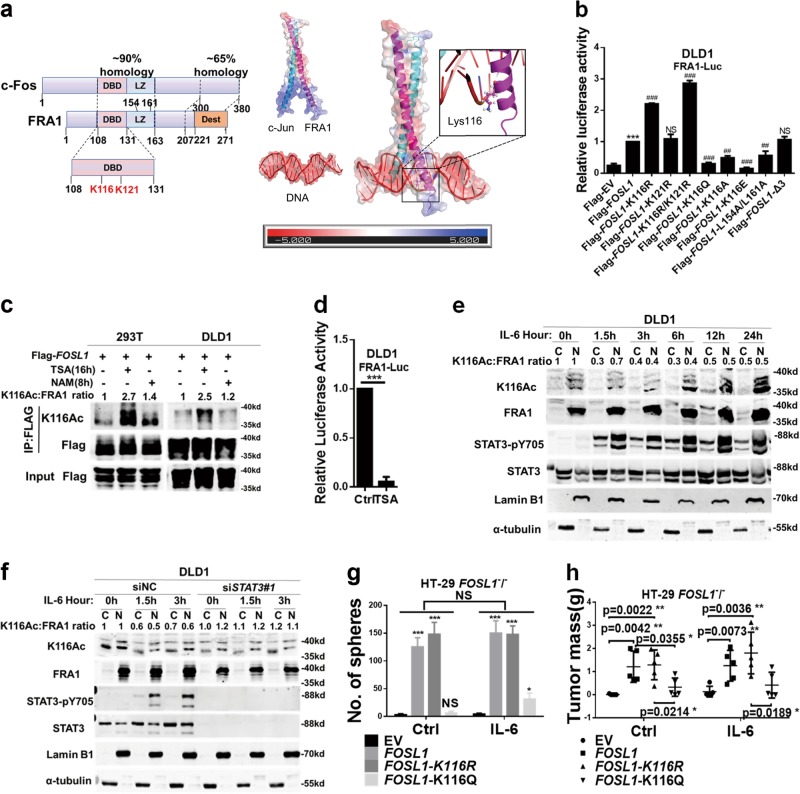
Fig. 2.
Interleukin (IL)-6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)-driven FRA1 Lys-116 deacetylation increases its transcriptional activity. a Left panel: schematic diagram of the homology between structural domains in c-Fos and FRA1. The highest homology is found in the DNA-binding domain that encompasses the two FRA1 acetylated lysine residues (K116 and K121) identified by mass spectrometry. Two leucine residues (L154 and L161) located in the Leucine zipper domain (LZ) were responsible for FRA1 heterodimerizing with the JUN family. Phosphorylation of many serine (S) or threonine (T) residues of FRA1 in destabilizer domain (DEST) increase its stability. Right panel: Charge density map of AP-1(c-Jun and FRA1), DNA and the complex. Lys116 in FRA1 chain is shown as sticks and spheres. b Relative luciferase activity in DLD1 cells co-transfected with wild-type and (deletion and point) mutant FOSL1 constructs, together with pRL-TK as an internal control reporter. Δ3 deletion and L154A/L161A mutant constructs were here employed as controls (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, compared with the Flag-EV; ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, compared with the Flag-FOSL1). c Immunoprecipitation (IP) analysis of FRA1 K116 acetylation. The Flag-FOSL1 construct was transfected into 293T and DLD1 cells, followed by treatment with the deacetylase inhibitors trichostatin A(TSA) or nicotinamide, and IP with antibodies directed against Flag. FRA1 acetylation was analyzed by western blot with the K116Ac-specific antibody. d FRA1 transcriptional activity in response to TSA treatment for 16 h and then measured by FRA1-Luc luciferase assay in DLD1 cells. e DLD1 cells were cultured in the presence of IL-6 for the indicated times and the cytoplasmic and nuclear protein fractions were separated for western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. K116 acetylation was detected with the K116Ac antibody and normalized against the FRA1 protein. (LaminB1 and α-tubulin were employed as nuclear and cytoplasmic protein control, respectively). f DLD1 cells were transfected with siNC or STAT3 small interfering RNAs and incubated with IL-6 for the indicated times. Cytoplasmic and nuclear protein fractions were separated for western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies. K116 acetylation was detected with K116Ac antibody and normalized against the FRA1 protein. g, h HT-29 FOSL1−/− cells were constructed by TALEN and transfected with expression constructs encompassing wild-type and mutated FOSL1. These cells were then analyzed for their capacity to form spheres in vitro (g) and to form subcutaneous tumors in vivo upon IL-6 stimulation (h). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Unpaired t test. Data are presented as mean ± SD