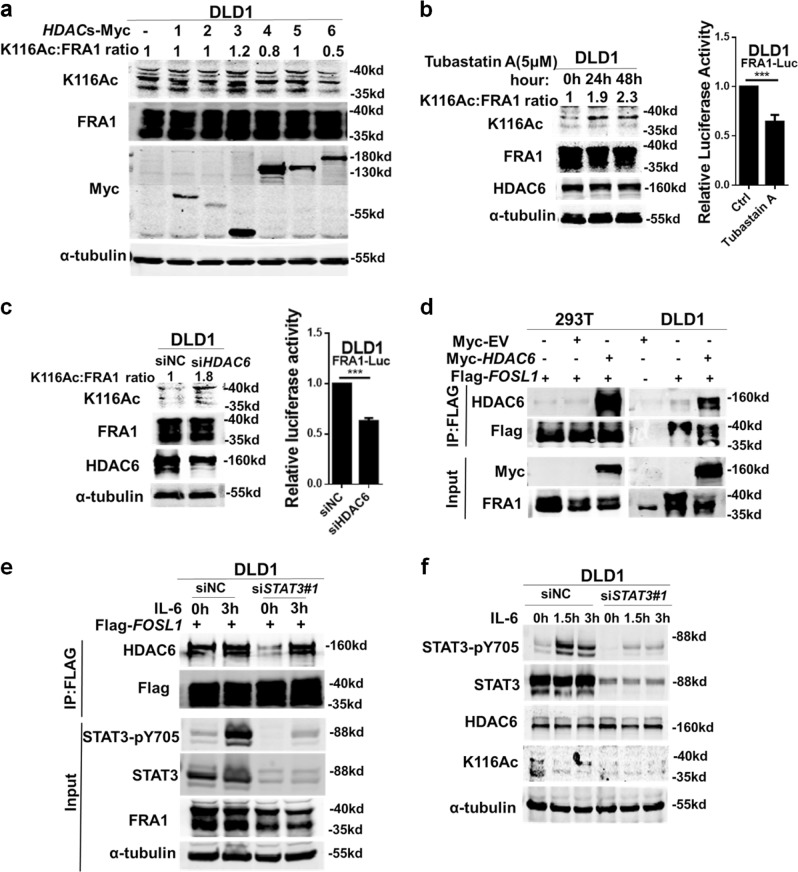
Fig. 3.
HDAC6 deacetylates FRA1 and underlies its transcriptional activation downstream of interleukin (IL)-6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). a Overexpression of HDAC6, but not of other HDACs, decreases FRA1 acetylation levels. Each of the Myc-tagged HDAC (1–6) were transfected into DLD1 cells and the K116 FRA1 acetylation levels were determined by western blotting with the K116Ac antibody and normalized against the FRA1 protein. b Western blot analysis and relative FRA1-luc reporter activities in DLD1 cells treated with the HDAC6 small inhibitor Tubastatin A for the indicated times. c Small interfering RNA (siRNA) oligonucleotides directed against HDAC6 were employed to transfect DLD1 cells. The levels of endogenous K116 acetylation, FRA1, and HDAC6 expression were analyzed by western blot. And the FRA1-luc reporter activity was assayed. d IP-Flag analysis of the interaction between FRA1 and HDAC6 in 293T and DLD1 cells transfected with the indicated plasmids. e DLD1 cells were transfected with Flag-FOSL1 and the indicated siRNAs, followed by IL-6 stimulation for 3 h. IP-Flag analysis of HDAC6 was performed to assess the role of the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway on the FRA1–HDAC6 interaction. f DLD1 cells were transfected with non-target control oligonucleotides (siNC) or STAT3 siRNAs and incubated with IL-6 for the indicated times. The levels of STAT3-pY705, STAT3, HDAC6, α-tubulin, and endogenous K116 acetylation protein were determined by western blot. ***p < 0.001. Unpaired t test. Data are presented as mean ± SD