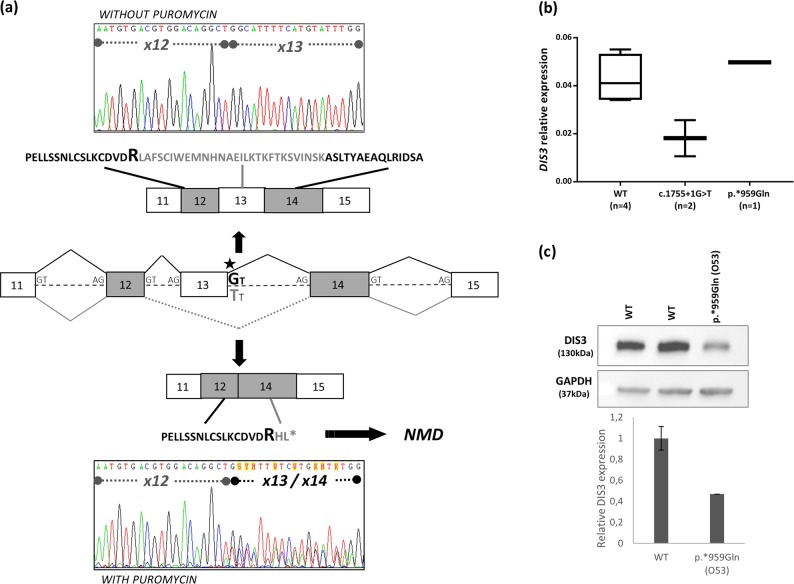
Fig. 2.
DIS3 c.1755+1G>T splicing variant results in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) and affects mRNA expression, while the c.2875C>T (p.*959Glnext*14) stop-loss variant affects protein levels. a LCLs from patients E18 and E28 (not shown) carrying the c.1755+1G>T splicing variant were cultured with and without puromycin. The chromatogram from treated cells (with puromycin) showed a mixture of the wild-type and mutant transcript lacking exon 13, which was not detected in the non-treated cells (without puromycin). Thus, the mutant transcript is degraded by NMD. b Box plot representing the relative DIS3 mRNA expression in c.1775+1G>A (n=2) and p.*959Glnext*14 (n = 1) carriers compared to non-carriers (n = 4). All reactions were performed in triplicates. c Western blot with an anti-DIS3 antibody was performed in LCLs from one p.*959Glnext*14 carrier and two wild-type individuals (anti-GAPDH antibody as internal control). The relative DIS3 expression in the p.*959Glnext*14 carrier was reduced by 50% compared to non-carriers, suggesting that the mutant allele is translated but degraded shortly after