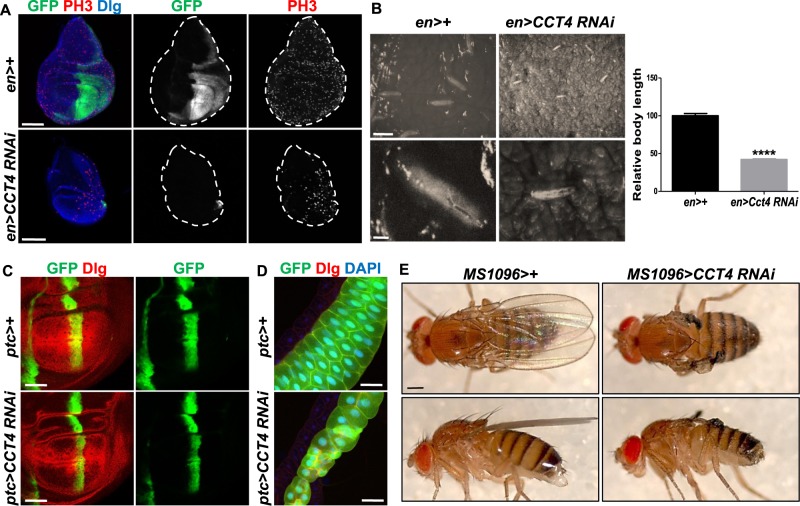
Fig. 2.
Knockdown of CCT4 reduces body size with developmental delay. a Wing disc of en>+ and en>CCT4 RNAi. en>CCT4 RNAi led to loss of the en-expressing posterior compartment (GFP positive). Scale bar, 100 μm. b Relative body length of 5-day-old larvae of en>+ and en>CCT4 RNAi. en>CCT4 RNAi larvae showed shorter body length than en>+ larvae. P-value was calculated by using two-tailed t-test. ****P < 0.0001. Scale bars, 5 mm (top) and 1 mm (bottom). n = 5 (en>+); 5 (en>CCT4 RNAi). c Wing disc of ptc>+ and ptc>CCT4 RNAi. ptc>CCT4 RNAi showed reduced tissue size in ptc-expressing area (GFP positive). Scale bars, 100 μm. d Salivary gland of ptc>+ and ptc>CCT4 RNAi. ptc>CCT4 RNAi caused abnormal development of salivary gland. Scale bars, 50 μm. e Adult wing of MS1096>+ and MS1096>CCT4 RNAi. MS1096>CCT4 RNAi resulted in near complete loss of adult wing. Scale bars, 500 μm