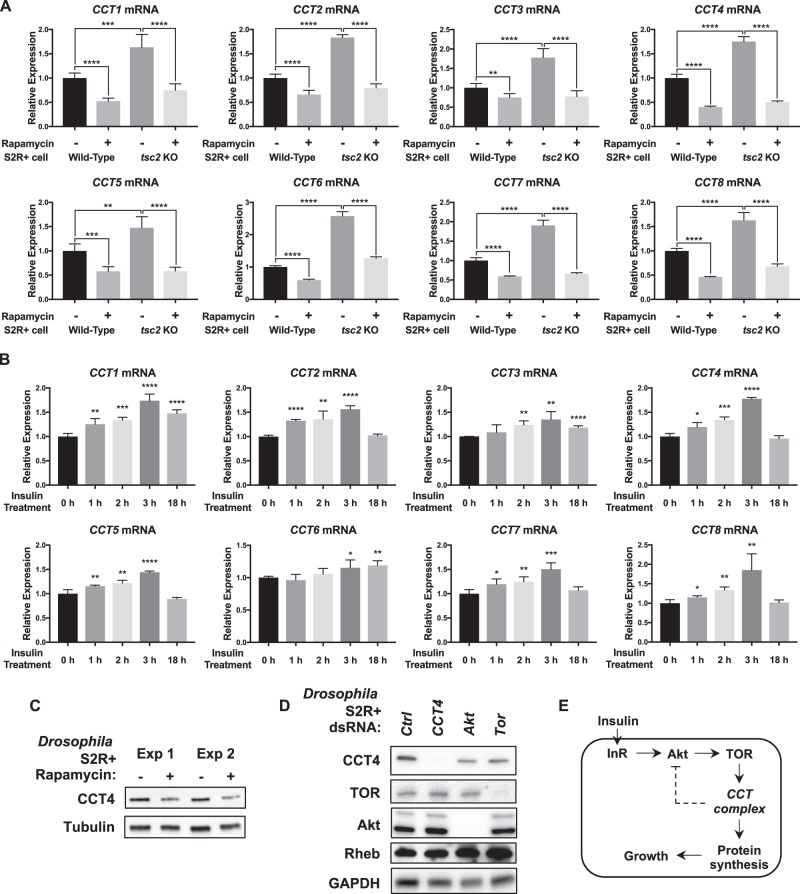
Fig. 8.
Insulin/TOR signaling activity affects the transcription levels of CCT complex. a Effects of rapamycin treatment on CCT mRNA levels in wild type and tsc2 KO S2R+ cells. Rapamycin (20 nM) was treated for 24 h. All CCT mRNA expressions were decreased by rapamycin treatment. All CCT mRNA expressions were higher in tsc2 KO cells compared to wild-type cells. Expression levels of CCT mRNA were normalized to Rp49 levels. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. n = 4. b Effects of insulin treatment on CCT mRNA levels in wild-type S2R+ cells. Insulin (25 µg/ml) was treated for the indicated time lengths. All CCT mRNA expressions were increased by 3 h insulin treatment. Some CCT mRNA levels were still elevated after 18 h insulin treatment. Expression levels of CCT mRNA were normalized to Rp49 levels. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. n = 4. c Rapamycin treatment decreases CCT4 protein levels. S2R+ cells were treated with rapamycin (20 nM) for 2 days. The same amounts of proteins were used for western blot. Two independent experiments were shown. Tubulin levels were used as loading controls. d Decrease in the CCT4 protein level of Akt or Tor-knockdown S2R+ cells. CCT4 protein levels were decreased when S2R+ cells were treated with Akt or Tor dsRNA. Protein levels of TOR, Akt, or Rheb were not changed by CCT4 RNAi. GAPDH levels were used as loading controls. e A proposed scheme of interaction between CCT complex and insulin/TOR signaling. Transcription of CCT complex is regulated by insulin/TOR signaling. CCT complex function is required for the downstream process of TOR signaling to facilitate protein synthesis essential for cellular growth. After activation of insulin/TOR signaling, CCT complex is required for negative feedback regulation of Akt activity