Fig. 2.
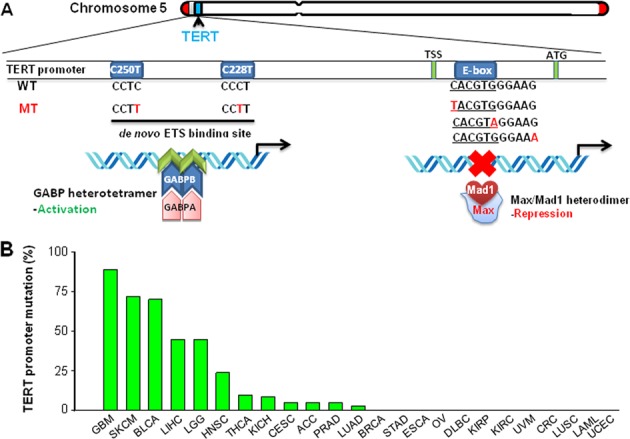
TERT promoter mutations in human cancer. a Schematic presentation of TERT promoter mutations and relevant transcription factors. The TERT gene at chromosome 5p and its promoter is shown. C > T mutation occurs at one of both positions of the TERT proximal promoter (−124 and −146 to ATG for C228T and C250T, respectively) in malignant cells, which create de novo ETS binding motifs. The ETS family members GABPA and GABPB form heterotetramers that bind to the de novo ETS site and activate TERT transcription. The E-box (CACGTG) sequence mutation was recently identified in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), which may lead to the dissociation of the repressor MAX/Mad1 complex from E-box, thereby de-repressing the TERT gene. b The frequency of TERT promoter mutations in a panel cancer types from the TCGA dataset analyses [49]. GBM glioblastoma multiforme, SKCM skin cutaneous melanoma, BLCA bladder urothelial carcinoma, LIHC liver hepatocellular carcinoma, LGG brain lower-grade glioma, HNSC head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, THCA thyroid carcinoma, KICH kidney chromophobe, CESC cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma, ACC adrenocortical carcinoma, PRAD prostate adenocarcinoma, LUAD lung adenocarcinoma, BRCA breast invasive carcinoma, STAD stomach adenocarcinoma, ESCA esophageal carcinoma, OV ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma, DLBC lymphoid neoplasm diffuse large B cell lymphoma, KIRP kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma, KIRC kidney renal clear cell carcinoma, UVM Uveal melanoma, SARC sarcoma, CRC colorectal carcinoma, LAML acute myeloid leukemia, LUSC lung squamous cell carcinoma, UCEC uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma
