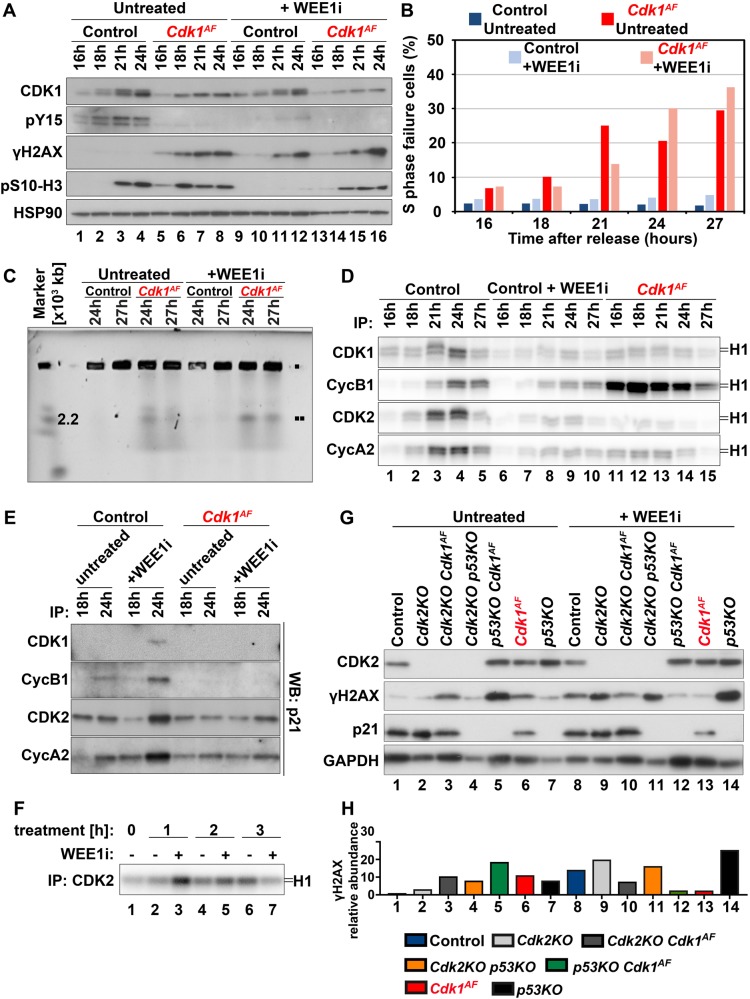
Fig. 6.
Different surveillance control mechanisms in WEE1-inhibited and Cdk1AF cells. Primary MEFs were synchronized at G0/G1 by serum starvation and then released into full serum medium in the presence or absence of WEE1i (1 μM). a Protein extracts from control (Cdk1flox/SAF) and Cdk1AF (Cdk1null/AF) MEFs treated with/without WEE1i were subjected to western blotting using the indicated antibodies. HSP90 served as a loading control. b S phase failure was determined by BrdU FACS, whereas in c DNA fragmentation was visualized by PFGE in all four experimental groups. d Protein extracts from (c) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with the indicated antibodies. Kinase activities of the immunoprecipitates were determined by in vitro kinase assays as previously described. e The abundance of p21 bound to different CDKs and cyclins was determined in protein lysates by co-immunoprecipitation with the indicated antibodies followed by western blotting against p21. f WEE1i was added to control MEFs at 21 h after release from serum starvation (time point 0). Cells were collected at the indicated time points (1, 2 and 3 h) in the presence or absence of WEE1i. Protein extracts were isolated and subjected to immunoprecipitation with CDK2 antibodies. Kinase activities associated with CDK2 were measured by in vitro kinase assays. g Protein extracts at the 27-hour time point from control (Cdk1flox/SAF), Cdk2KO, Cdk2KO Cdk1AF (Cdk2KO Cdk1null/AF), Cdk2KO p53KO, p53KO Cdk1AF (p53KO Cdk1null/AF), Cdk1AF (Cdk1null/AF) and p53KO cells. MEFs treated with/without WEE1i were subjected to western blotting using the indicated antibodies. GAPDH served as a loading control. h Relative abundance of γH2AX and in samples presented in panel (g) upon previous normalization to GAPDH