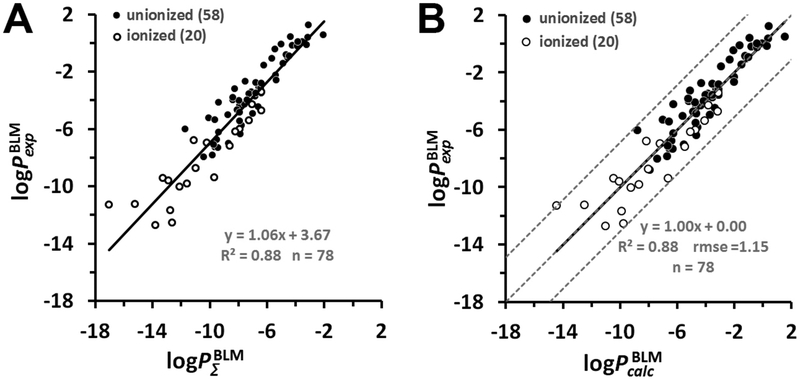
Figure 2.
Prediction of the permeability of artificial lipid bilayers to organic molecules. (A) Comparison of experimental and calculated permeability coefficients across unilamellar lipid bilayers of 58 un-ionized (black circles) and 20 ionized in water (open circles) organic molecules. The corresponding data values are from Tables S1 and S2. (B) Plot of experimental BLM permeability coefficients vs the calculated ones for 78 organic molecules. Dashed lines indicate ideal line and residual line limits (using a cutoff of |3.1| that corresponds to 2.0 rmse for ionized molecules). Predicted permeability coefficients, , in B were calculated using eq 15. The values were calculated using eq 6. For ionized species, the integral accounted for the deionization penalty of ionizable groups at the specified pH. The number of molecules “n” is indicated in parentheses.