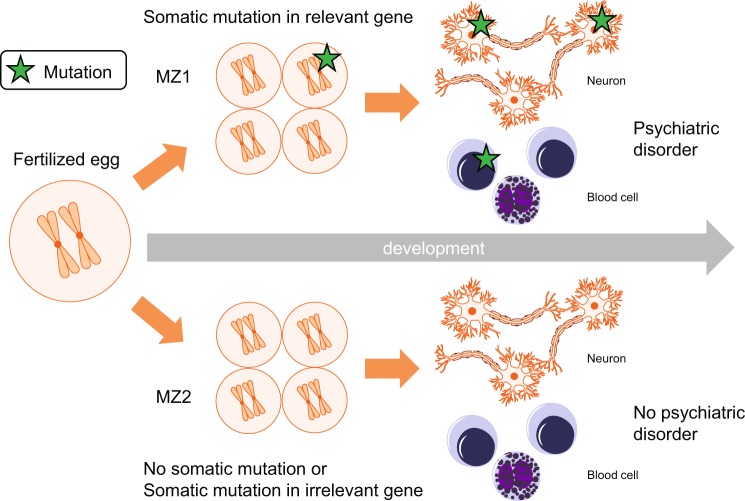
Fig. 2.
Somatic mutation model explaining phenotypic differences between monozygotic (MZ) twins. MZ twins have identical genomes at the time of fertilization, but somatic mutation profiles diverge after fertilization. Somatic mutations during development may underlie phenotypic differences between the twins, including discordant risk for psychiatric disorders. In this illustrated model, MZ1 has somatic mutations in the relevant genes in development, which are shared between the neurons and blood cells, and has a psychiatric diagnosis. MZ2 has no somatic mutations in the relevant genes does not have a psychiatric diagnosis