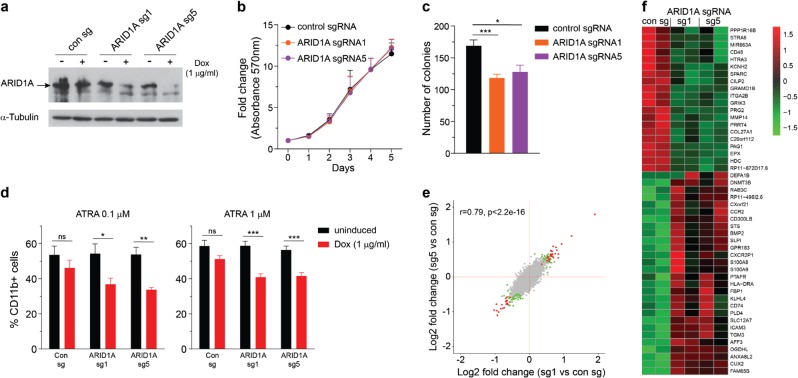
Fig. 7.
Loss of ARID1A impairs granulocytic differentiation of NB4 cells. a Immunoblot shows doxycycline (Dox) induced knockout of ARID1A in NB4 cells expressing Cas9 and sgRNA targeting ARID1A. Protein lysate from NB4 cells treated with doxycycline for 7 days were analyzed. b Viability of ARID1A-deficient and control NB4 cells was determined using MTT reagent (n = 5). c Colony-forming ability of ARID1A knockout NB4 cells compared with control cells. Cells were plated in media containing methylcellulose, and colonies were enumerated after 9–11 days (n = 6). d Percentage of CD11b-expressing cells at 48 h after treatment with 0.1 (n = 5) and 1 µm ATRA (n = 7). e Correlation plot compares expression profiles of Dox-treated ARID1A sg1 and sg5 NB4 cells compared to Dox-treated control cells. Genes significantly upregulated or downregulated (FDR < 0.1; absolute log2 fold change > 0.1) in both sg1- and sg5-expressing NB4 cells are shown in red and those which are significantly altered with only one sgRNA are depicted in green. f Heat map shows differential expression of genes significantly altered in both Dox-treated ARID1A sg1 and sg5 expressing NB4 cells compared to the Dox-treated control cells (FDR < 0.1). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns = not significant