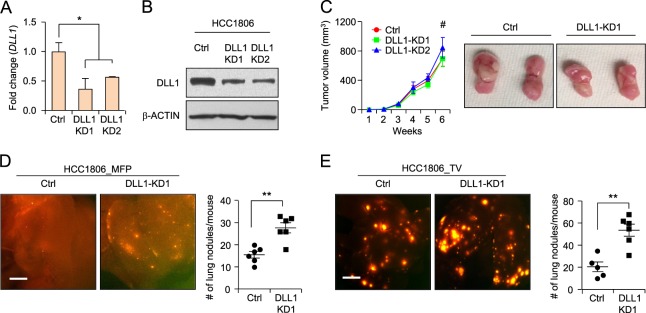
Fig. 3.
DLL1 does not influence tumor growth but inhibits metastasis in human TNBC. a, b qPCR and western blot data show DLL1 mRNA and protein levels in human TNBC cell line HCC1806 after lentivirus-mediated knockdown (KD) of DLL1. c 200,000 HCC1806 control and DLL1-KDs (KD1 and KD2) cells were injected into mammary fat pad of NSG mice. Tumor growth curves (c, left) and representative whole tumor images (c, right) show no significant difference in growth of HCC1806 DLL1-KDs (KD1 and KD2) primary tumors compared to control, n = 6 mice used per group. d Representative whole mount images of lungs from mice with mammary fat pad injection (MFP) show metastasis as seen by RFP positivity (d, left) and respective quantification is shown in (d, right). e 200,000 HCC1806 control and DLL1-KD1 tumor cells were injected into blood stream of NSG mice through tail-vein. Lung metastasis as seen by RFP+ nodules show higher number of RFP+ lung nodules in DLL1-KD1 compared to control (e, left). Quantification is shown in (e, right). n = 5 mice (Ctrl) and n = 6 mice (DLL1-KD1) were used. d, e Mann−Whitney U test and c two-way ANOVA test with Bonferroni correction was performed to compute statistical significance. Scale bars, 500 µm in (d, e). a Data are presented as the mean ± SD. c−e Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and #nonsignificant