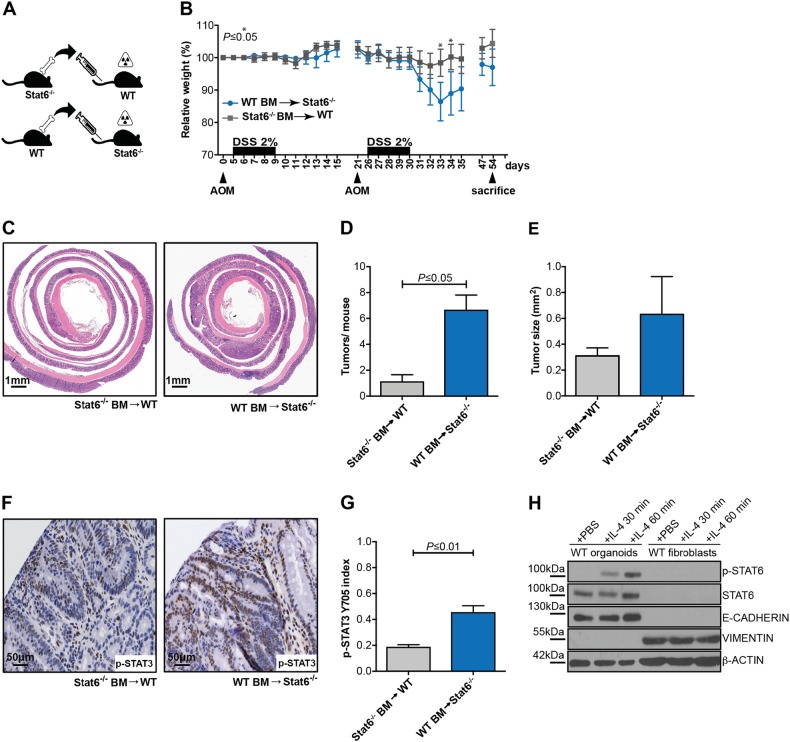
Fig. 3.
Stat6 expression in intestinal epithelial cells prevents inflammation-associated carcinogenesis a–h. a Stat6−/−BM > WT or WT BM > Stat6−/− reconstituted mice were challenged with the CAC model; b Weight changes of transplanted mice during AOM/DSS model; c Representative H&E stained sections of Stat6−/−BM > WT and WT BM > Stat6−/− mice colonic tumors; d, e Tumor incidence and tumor size in Stat6−/−BM > WT and WT BM > Stat6−/− mice at the end of the CAC model (Stat6−/−BM > WT n = 7; WT BM > Stat6−/− n = 6); f, g Immunohistochemical analysis and quantification of p-STAT3 Y705 in tumors from Stat6−/−BM > WT and WT BM > Stat6−/− mice (n = 3/genotype); h Immunoblot analysis of p-STAT6 Y641 from WT colon organoids and fibroblast lysates stimulated with recombinant mouse IL-4 for 30 and 60 min. E-cadherin and Vimentin antibodies were used to ensure the respective epithelial and mesenchymal origin of the samples. β-actin as loading control. Data are mean ± SEM