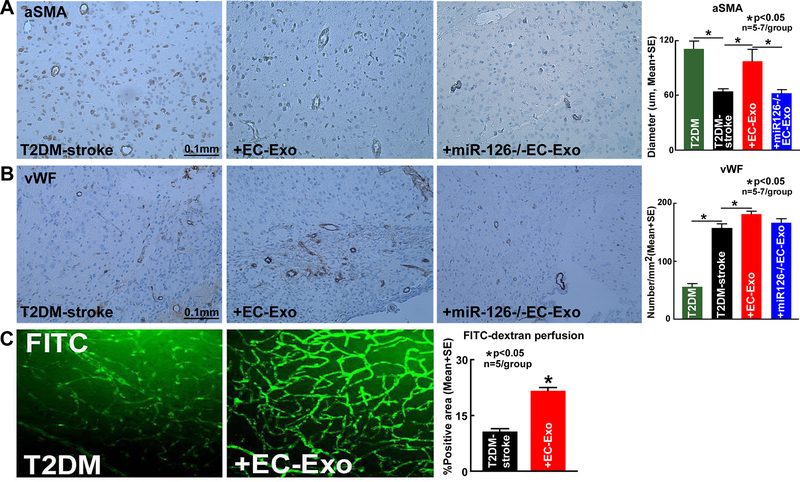
Figure 4. EC-Exo promotes vascular remodeling and increases vessel patency in T2DM-stroke mice.
(A-B) Stroke in T2DM mice significantly decreases arterial diameter and increases vascular density comapred to non-stroke T2DM control mice. EC-Exo treatment of T2DM-stroke mice significantly increases arterial diameter and vascular density in the cortex and striatum of the IBZ. Loss of miR-126 in EC-Exo attenuates EC-Exo induced vascular remodeling in T2DM-stroke mice. (C) EC-Exo treatment significantly increases vessel patency indicated by increased FITC-dextran vascular perfusion in the cortex, striatum and corpus callosum of the IBZ of T2DM-stroke mice at 14 days after stroke.