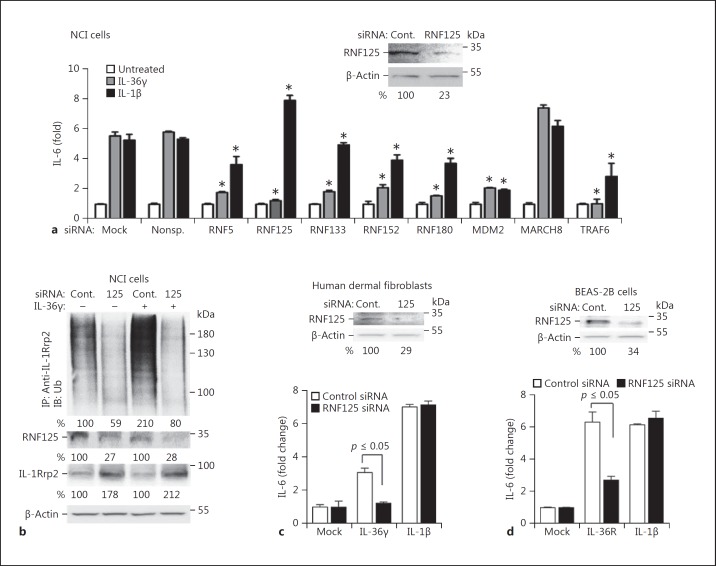
Fig. 2.
RNF125 regulates IL-36R signaling. a Sample results of the knockdown of E3 ubiquitin ligases and their effect on IL-36R and IL-1R signaling in NCI cells. Knockdown used 50 nM siRNA specific to E3 ubiquitin ligases or a nonspecific control siRNA. The siRNA specific to RNF125 was a mixture of 4 independently synthesized siRNAs. The cells were incubated for 48 h following transfection of the siRNAs and further treated with IL-36γ (1 ng/mL). Cell media were collected 24 h later for quantification of IL-6 by ELISA. A comparison of the amount of IL-6 produced relative to the samples treated with nonspecific RNA was calculated using the Student t test. * p ≤ 0.05 calculated from 2 experiments with 6 independent samples. Western blots are shown (above) of the accumulation of RNF125 and the β-actin loading controls in NCI cells knocked down with siRNAs specific to RNF125 or with control siRNAs. All Western blot data shown are representative of 3 independent experiments. b RNF125 affects polyubiquitination on IL-1Rrp2 in NCI cells. Immunoprecipitation of IL-1Rrp2 from cell lysate was from cells transfected with RNF125 siRNA. Ubiquitin associated with IL-1Rrp2 was detected using Western blot analysis. The amount of the RNF-125, IL-1Rrp2, and β-actin in the samples used for the analysis of ubiquitinated IL-1Rrp2 were determined by Western blots. c Knockdown of RNF125 results in defective IL-36R signaling in HDF. The mean levels of IL-6 production by IL-36R signaling from 3 independent experiments are shown. Western blots are included (above) of the accumulation of RNF125 and the β-actin loading controls in HDF cells knocked down with siRNAs specific to RNF125 or with control siRNAs. The Western blot data shown are representative of 3 independent experiments. d Effect of RNF125 knockdown on IL-36R signaling in BEAS-2B cells. The results are representative of 3 independent experiments. Western blots are shown (above) of the accumulation of RNF125 and the β-actin loading controls in BEAS-2B cells knocked down with siRNAs specific to RNF125 or with control siRNAs.