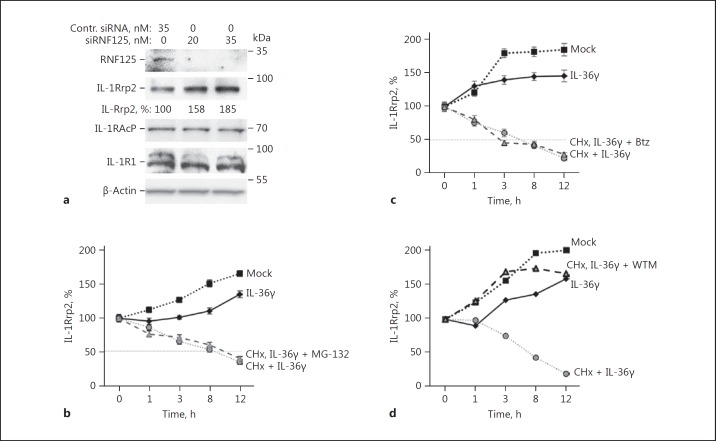
Fig. 4.
RNF125 promotes the turnover of IL-1Rrp2. a Knockdown of RNF125 increases the accumulation of IL-1Rrp2 in NCI cells. Knockdown used either 20 or 35 nM of RNF125 siRNA and cells were treated with IL-36γ. The knockdown of RNF125 did not affect the accumulation of the IL-36R accessory protein, IL-1RAcp. The total concentration of siRNA transfected into cells was normalized by the addition of nonspecific control siRNA. Comparable increases in the accumulation of IL-1Rrp2 were observed in 3 independent experiments. b IL-1Rrp2 accumulation in NCI cells was not affected by inhibiting the proteasome. The accumulation of IL-1Rrp2 relative to β-actin was quantified from Western blots following treatment with either IL-36γ (10 ng/mL) alone or in combination with protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide (60 μg/mL) and proteasome inhibitor MG-132 (5 μM). Each data point represents the mean and 1 standard error from a sample tested in 3 independent experiments. c The 26S proteasome inhibitor Btz (30 nM final concentration) also did not affect IL-1Rrp2 accumulation after agonist activation of the IL-36R. d Endosome trafficking inhibitor WTM inhibited IL-1Rrp2 turnover. WTM was added to the cells to a final concentration of 100 nM. The results are representative of 2 independent experiments.