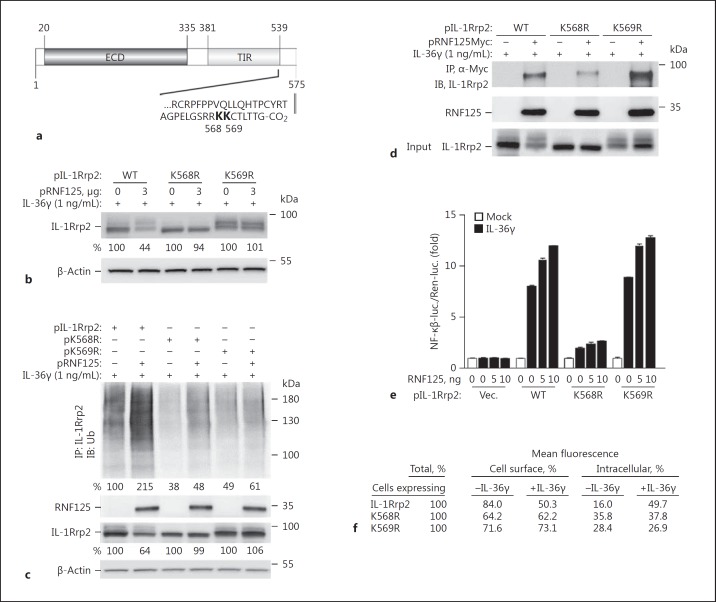
Fig. 7.
The C-terminal tail of IL-1Rrp2 mediates RNF125 binding, ubiquitination, and signaling in HEK293T cells. a Location of predicted ubiquitination sites in IL-1Rrp2. The prediction used the IPM algorithm [36]. b Mutants K568R and K569R accumulated to higher levels in HEK293T cells overexpressing RNF125. HEK293T cells were transfected with 1 μg each of plasmids expressing IL-1Rrp2, K568R, or K569R, and 3 μg of pRNF125. c K568R and K569R have decreased polyubiquitination. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing IL-1Rrp2 (1 μg) and pRNF125 (0.75 μg) for 36 h. Polyubiquitination was determined by immunoprecipitation of IL-1Rrp2 and Western blots probed with an antibody that recognizes ubiquitin. d IL-1Rrp2 mutants K568R and K569R were also tested for binding to RNF125 upon immunoprecipitation with antibody to the c-Myc sequence followed by Western blots to probe IL-1Rrp2 and RNF125. e IL-36R with the K568R was defective for signal transduction. Signal transduction was performed using the luciferase reporter assay upon treatment of IL-36γ for 12 h after 3 h of plasmid transfection. All data represent the means of 3 independent experiments. WT, wild-type. f Abundance of IL-1Rrp2 and the ubiquitination mutants on the surface of HEK293T cells. Cell surface levels of the proteins were quantified using flow cytometry. The numbers shown are the relative mean fluorescence of the gated cells.