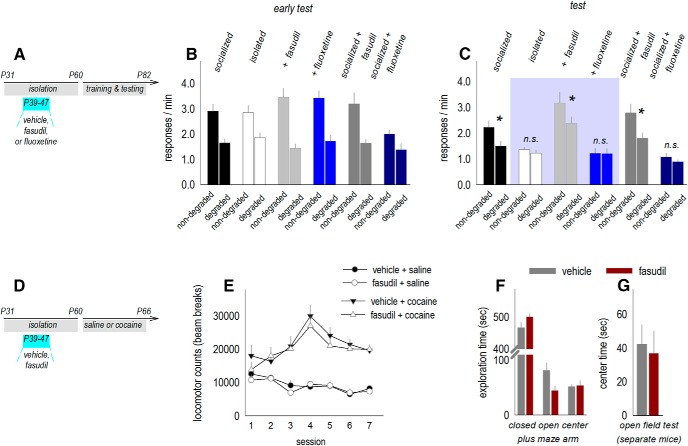
Figure 8.
ROCK inhibition normalizes instrumental response updating following social isolation. A, Timeline: mice were socially housed or isolated in adolescence (P31–P60) and treated (from P39 to P47) with vehicle, fasudil, or FLX. B, As adults, mice were trained to nose poke for food reinforcers, and as in prior figures, all mice were initially sensitive to instrumental contingencies, inhibiting responding when it was unlikely to be reinforced (n = 19 total group control; n = 17 total isolation-housed control; other groups n = 8–10). C, Subsequently, adult mice exposed to isolation during adolescence failed to update response strategies as expected (test). ROCK inhibition by fasudil rescued response strategies, while adolescent FLX promoted failures in response updating. Key comparisons are highlighted. D, Timeline: mice were socially housed or isolated in adolescence (P31–P60) and treated (from P39 to P47) with vehicle or fasudil. As adults, locomotor sensitivity to repeated cocaine was tested. E, Fasudil did not obviously impact the development of cocaine-induced locomotor sensitization (n = 8/group). Exploration of an elevated plus maze (F) and open field (G) were also not affected (n = 7/group, tested in separate cohorts of mice). Mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05. n.s., non-significant.