FIGURE 1.
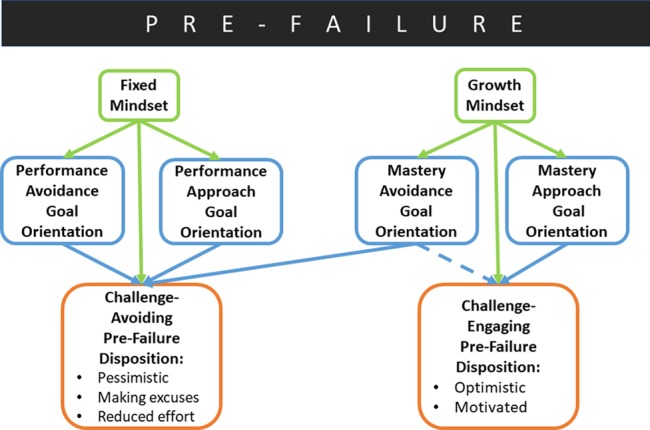
Minimodel 1: mindset and goal orientations. Predicted relationships between mindset (green), goal orientation (blue), and prefailure disposition (orange) for undergraduate STEM contexts. Solid lines represent relationships with empirical support in the literature, primarily drawn from contexts outside undergraduate STEM learning (Supplemental Figure 1). Dashed lines represent relationships without empirical support. Growth mindset leads to a challenge-engaging prefailure disposition; fixed mindset, by contrast, leads to a challenge-avoiding prefailure disposition. Growth mindset leads to mastery goal orientations, while fixed mindset leads to performance goal orientations. Performance goals lead to a challenge-avoiding disposition. Mastery-approach goals lead to a challenge-engaging disposition and mastery-avoidance goals tend to lead to challenge-avoiding dispositions. We predict, however, that some individuals with mastery-avoidance goals may express challenge-engaging disposition (dashed line).
