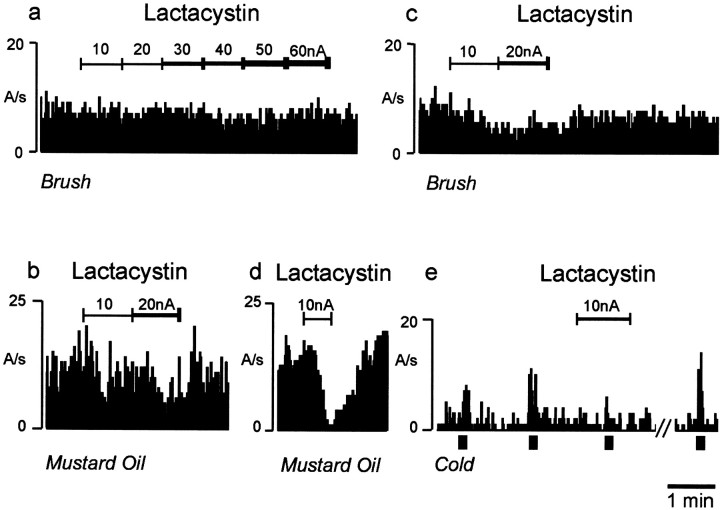
Fig. 1.
Typical effects of ionophoretic application of the proteasome inhibitor lactacystin on stimulus-evoked sensory responses of single dorsal horn neurons in naive and neuropathic animals. In naive animals, lactacystin had no effect on brush-evoked activation of dorsal horn neuron cell firing rate, measured as action potentials per second (A/s), but it caused a selective attenuation of mustard oil-evoked activation of dorsal horn neuron cell firing (a, b). In contrast, in neuropathic animals, lactacystin reduced dorsal horn neuron firing evoked by application of brush, mustard oil, and cold stimuli to the neuronal receptive field area (c–e). Thebar (bottom right) indicates 1 min duration. Lines above the firing records indicate the duration of the drug application by ionophoresis, close to the recorded cell. This is measured in nanoamperes (nA) of current used to eject the drug and was increased sequentially by 10 nA every 1–2 min.