Fig. 6.
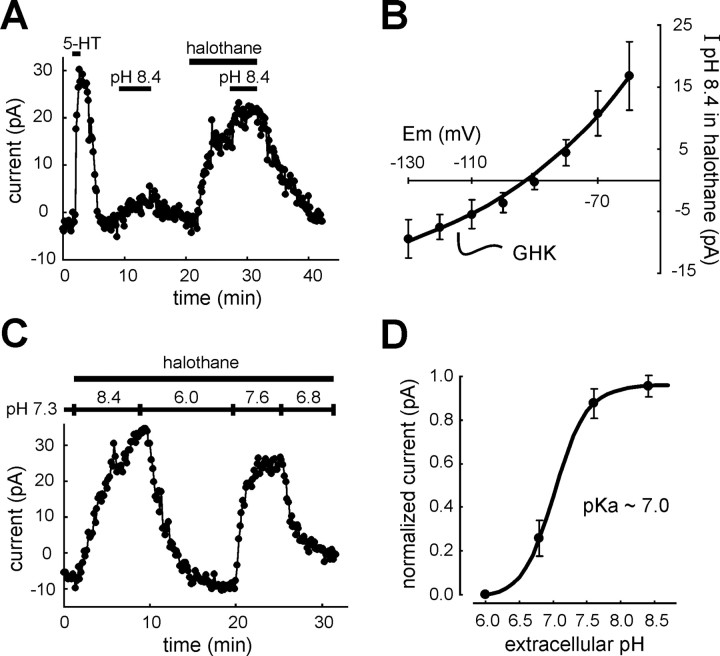
The pH- and anesthetic-sensitive current in RDo has a pH sensitivity intermediate between TASK-1 and TASK-3.A, Voltage-clamp recording in a serotonergic dorsal raphe neuron. 5-HT (100 μm) induced an outward shift in membrane current at −60 mV that is characteristic of serotonergic RDo neurons. Bath alkalization (from pH 7.3 to pH 8.4) evoked an outward current under control conditions and in the presence of halothane (1.25 mm). B, Averaged data depicting theI–V relationship of the current evoked by alkalized solution in halothane; these data were well fitted with the GHK constant field equation (±SEM; n = 11).C, To determine the pH sensitivity of currents in RDo neurons, the extracellular pH was varied between pH 6.0 and pH 8.4 in the continued presence of halothane (to enhance the amplitude of pH-sensitive currents). D, For each cell, currents measured under these pH conditions were normalized to the maximum and minimum current, and those normalized data were fitted to a logistic equation that predicted a pK of ∼7.0 for the pH- and halothane-sensitive dorsal raphe current. This value is intermediate between those measured for cloned rTASK-1 and rTASK-3 (∼7.4 and 6.7, respectively).