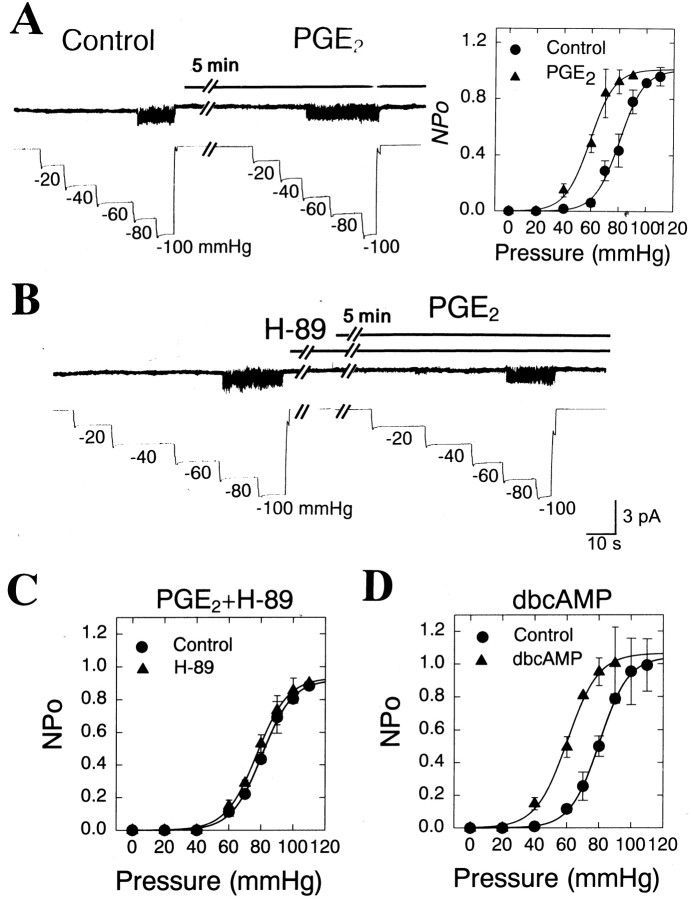
Fig. 7.
Sensitization of HT MS channel by PGE2via the protein kinase A pathway. A, Negative pressures were repeated in cell-attached patches at a holding potential of −60 mV. Before and during the second application of suction pressures, the cell-attached patches of sensory neurons were incubated with 10 μm PGE2 for ∼5 min. Right,The pressure-activity relationships of HT MS channels before (circle;n = 6–14) and after PGE2 (triangle;n = 6–14) treatment. Channel activity (NPo) at each pressure was fitted to the Boltzmann distribution described in the text. Bars represent SEM.B, Block of the PGE2-induced sensitization of HT channels by H-89, an inhibitor of protein kinase A. H-89 (10 μm) was incubated before and during PGE2application. C, A summary of the effect of coapplication of H-89 and PGE2 on the pressure-response relationship of HT MS channels. Control (circle;n = 5–10), after H-89 treatment (triangle;n = 5–10). D, A summary of the effect of the application of dibutyryl cAMP (dbcAMP), a soluble cAMP analog, on the pressure-response relationship of HT MS channels. Control (circle;n = 5–10), after dbcAMP treatment (triangle; n = 5–10).