Fig. 4.
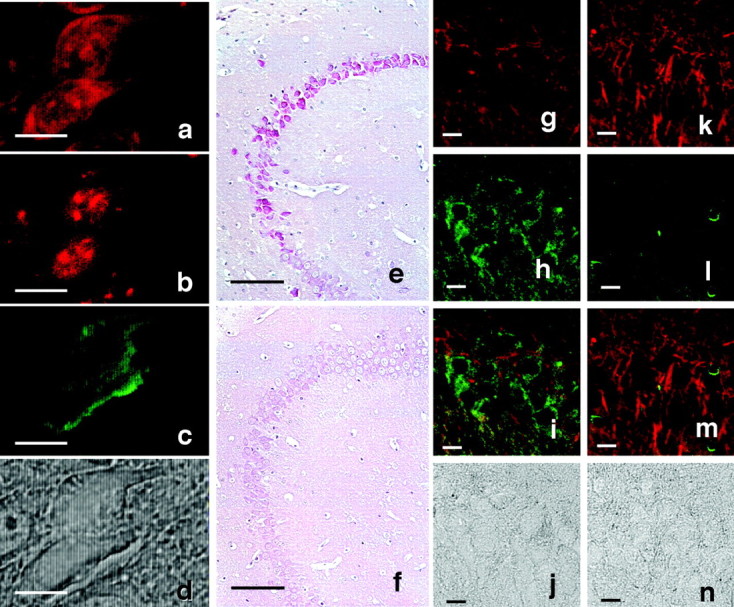
RNA accumulation and lack of microtubules in irregularly shaped neurons. a–d, Image of a thioflavin-S–PI-labeled neuron from the hippocampus of a 10-month-old Tg214 mouse. a, b, PI labeling (red); c, thioflavin-S (green); PI staining without RNase pretreatment (a) and with RNase pretreatment (b). In b andc note that in the same sections shown ina pretreated with RNase, PI stained only nuclei, and only thioflavin-S staining was observed in the cytoplasm.e, f, RNA accumulation in hippocampal neurons of 11-month-old Tg mice and non-Tg littermates. Methyl green–pyronin staining was performed using brain sections from Tg214 mice (e), and non-Tg littermates (f). RNA accumulation was detected in Tg214 neurons located in identical locations where Congo Red birefringent neurons were observed. g–n, Lack of microtubules in irregularly shaped neurons. g–j, Tg214 mouse (11 month). k–n, Non-Tg littermate (11 month).g, k, Image of anti-α tubulin-immunostained neurons (red). h,l, Image of phosphorylation-dependent anti-tau PS199-immunostained neurons (green).i, m, Merged image of gand h showing a nonoverlap of phosphorylation-dependent tau immunoreactivity (green) with α tubulin immunoreactivity (red). j,n, Phase-contrast photomicrograph of the same area shown in g–i and k–m. Irregularly shaped neurons lose tubulin immunoreactivity, but retain phosphorylated tau immunoreactivity. Scale bars: a–d, 10 μm;e, f, 100 μm; g–n, 10 μm.
