Fig. 8.
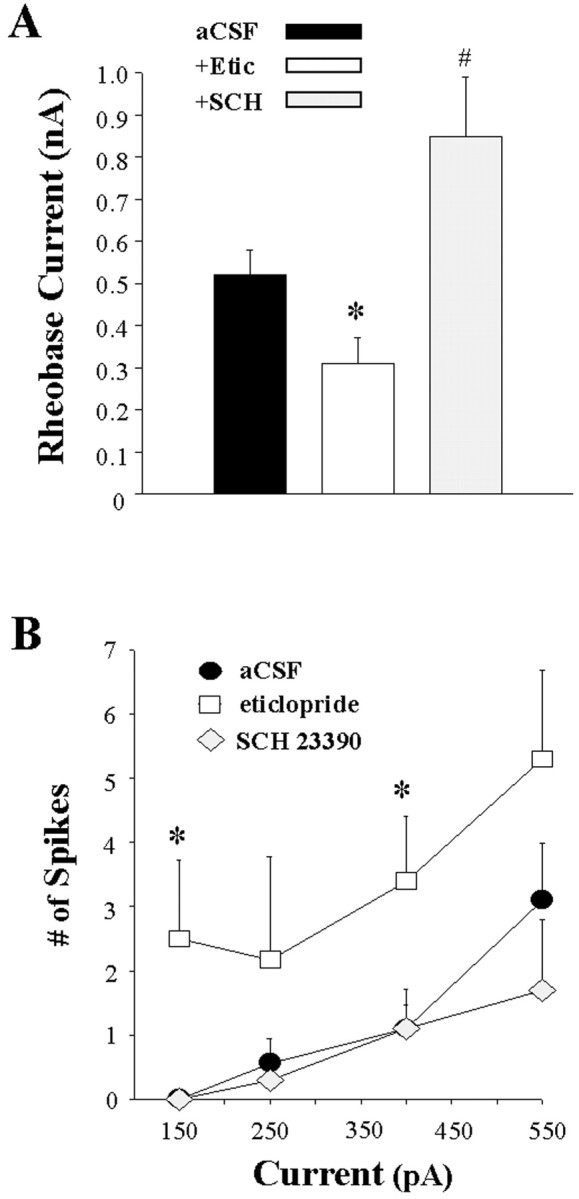
Opposite effects of local D1 and D2 antagonist infusion on activity evoked by intracellular injection of depolarizing current. The mean ± SEM rheobase current and number of spikes evoked by current steps of increasing intensity were determined in separate populations of striatal neurons recorded during intrastriatal aCSF, eticlopride (20 μm), or SCH 23390 (10 μm) infusion (5–90 min). Comparisons of the above measures of neuronal activity were made among the aCSF control (n = 19 cells), eticlopride (n = 10 cells), and SCH 23390 (n = 10) groups using a one-way ANOVA.A, Eticlopride infusion induced a decrease in the minimal current amplitude required to reach threshold (*p < 0.05; ANOVA, Dunn's test), whereas SCH 23390 was observed to increase the rheobase current (#p < 0.05; ANOVA, Dunn's test).B, An overall increase in the number of spikes elicited for a given current intensity was observed after eticlopride infusion (*p < 0.05; ANOVA, Dunnett's test), whereas SCH 23390 was without effect (p > 0.05).
