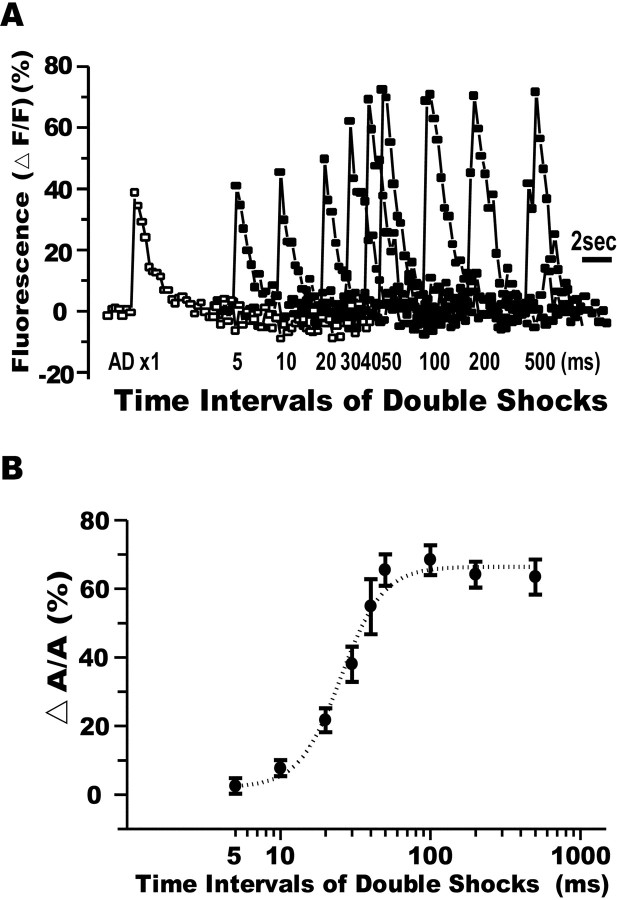
Fig. 6.
Time course of the inhibitory shunt of an M-cell.A, Superimposed traces of the Ca2+responses (filled squares) evoked in an M-cell by double AD shocks spaced at the intervals denoted below. The peak Ca2+ response elicited by double AD shocks was attenuated when the interval was <50 msec. Note that the peak amplitude for an interval of 5 msec was quite similar to that evoked by a single pulse (AD ×1, open squares). A notch was observed in the rising phase of the Ca2+response at an interval of 500 msec, because the second Ca2+ elevation was combined with the decay phase of the first response, as shown in Fig. 4B.B, Relationship between the ratio of an additional increase of Ca2+ response (ΔA) evoked by the second pulse and that by a single pulse (A, y-axis) and intervals of double pulses (x-axis, in log scale) summarized from 11 fish. The dotted line expresses the Boltzmann fit to the data. The half-recovery time was 25.3 ± 2.5 msec. The effective periods of the inhibitory shunt resemble those obtained in previous electrophysiological studies (cf. Furukawa and Furshpan, 1963; Faber and Korn, 1982; Oda et al., 1995, 1998; Hatta and Korn, 1998).