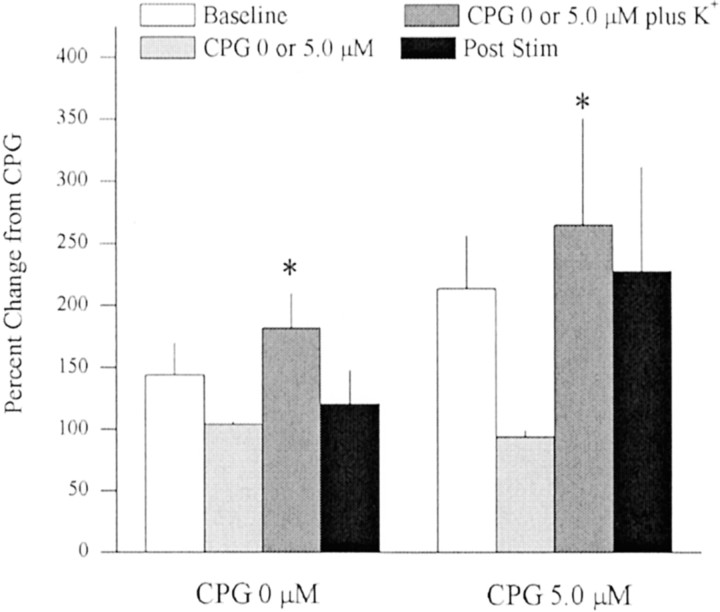
Fig. 3.
In vivo microdialysis was used to sample extrasynaptic glutamate in the striatum after reverse dialysis of K+ alone (i.e., 0 μm CPG + K+; n = 8) or after reverse dialysis of 5.0 μm CPG followed by 5.0 μmCPG plus K+ (80 mm;n = 8). Mean extracellular glutamate levels (± SEM) in the 0 μm CPG experiment were 1.83 ± 0.36 μm during baseline and 1.52 ± 0.28 μmduring 0 μm CPG. The decrease in extracellular glutamate during the 0 μm CPG treatment was not significantly different from baseline and was essentially caused by a single rat that exhibited stable basal levels but exhibited a drop in glutamate while switching dialysis buffer. In the 5.0 μm CPG experiment, extracellular glutamate levels were 2.01 ± 0.41 μmduring baseline and 1.33 ± 0.24 during 5.0 μm CPG. Because 5.0 μm CPG lowered extracellular glutamate levels, the data presented are normalized to glutamate levels at 0 or 5.0 μm CPG. A two-way ANOVA on glutamate levels across time between rats treated with 0 or 5.0 μm CPG indicated a significant effect of time (F(3,42) = 3.337; p < 0.05). *p < 0.05, difference from respective CPG baseline (0 or 5.0 μm; Fisher's LSD post hoc analysis).