Fig. 7.
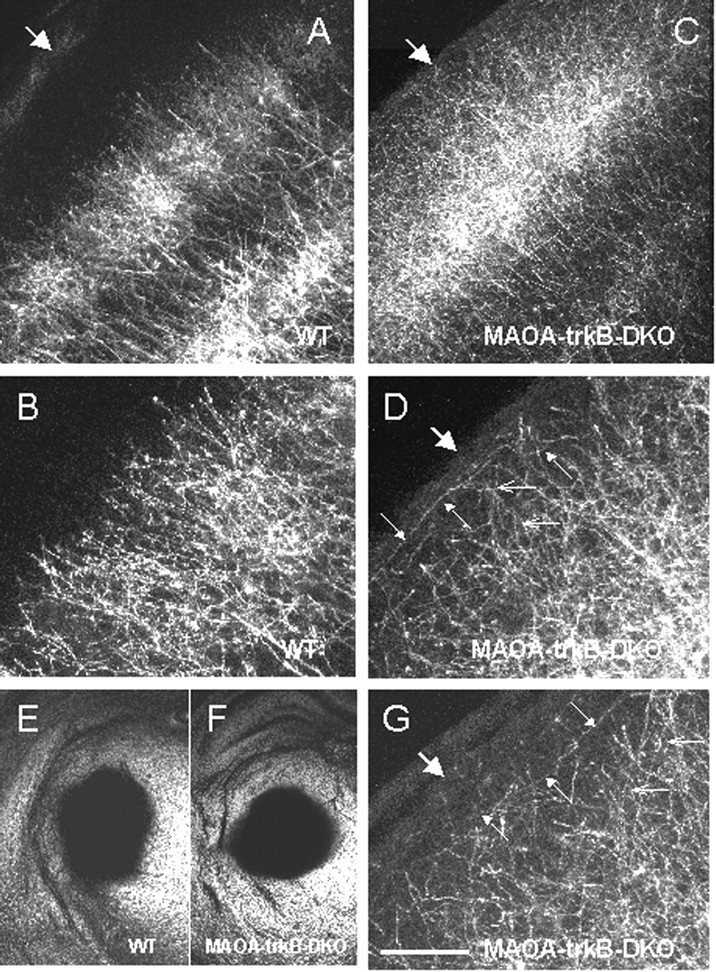
DiI tracing of thalamocortical axons in wild-type (WT) (A,B, E) and MAOA-trkB-DKO (C, D, F,G) pups at P8. A, B, In wild type, thalamocortical axons are clustered into barrels, and their terminals are mainly restricted to layer IV and do not massively extend in the supragranular layers. B, Higher magnification ofA. C, D, G, In MAOA-trkB-DKO mice, thalamocortical axons densely innervate layer IV but also supragranular layers II–III. D, Higher magnification of C. G, Higher magnification of a section taken from another MAOA-trkB-DKO pup.D, G, Small open arrowspoint to portions of axons that are oriented perpendicular to the pial surface. Small filled arrows point to portions of ectopic thalamocortical axons that are oriented parallel to the pial surface in layers I–III (D, G).A–D, G, Large arrowsindicate the pia. E, F, Bright-field photomicrographs of coronal sections showing the area of DiI diffusion in the thalamus of the wild-type pup (E) and the MAOA-trkB-DKO pup (F) shown in A,B and C, D respectively. These sections are 400 μm rostral to the site of injections. Scale bar: A, C, 150 μm; B,D, G, 60 μm; E,F, 2 mm.
