Fig. 2.
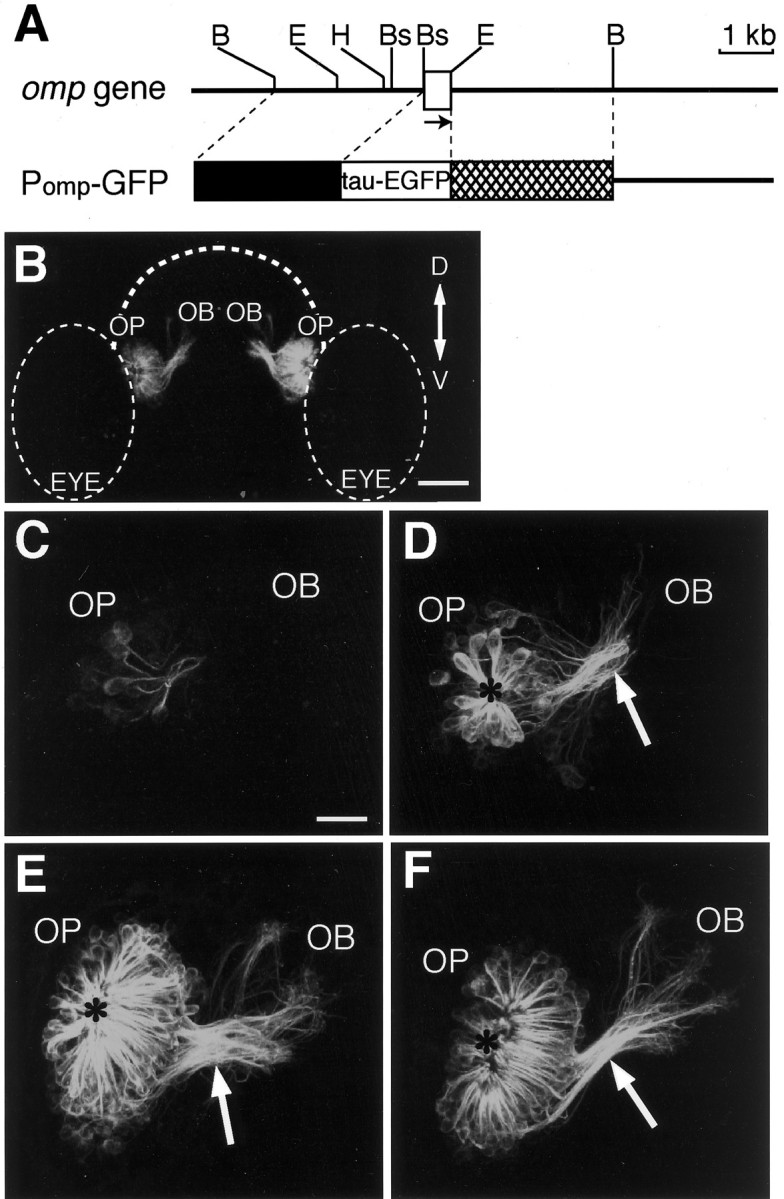
Axon extension of olfactory sensory neurons in living zebrafish carrying the omp promoter-driven tau-EGFP transgene. A, Genomic structure and restriction map of the zebrafish omp gene (top) and the structure of the omp promoter-driven tau-EGFP expression vector Pomp-GFP (bottom). Abox indicates the coding region of the zebrafishomp gene. The arrow shows the direction of the transcription. B, Bs,E, and H represent the restriction sites for BglII, BspLU11I,EcoRI, and HindIII, respectively. The line of Pomp-GFP vector indicates the sequence of the pBluescript II SK+. The 2.7 kb BglII–BspLU11I upstream sequence and the 3.0 kb EcoRI–BglII downstream sequence of the omp gene were used to drive tau-EGFP expression. B, Anterior view of the head of a transgenic zebrafish embryo at 72 hpf. The composite image is generated from the series of optical sections and oriented to correspond to the composite images shown in C–F. Dorsal (D) is to the top; ventral (V) is to thebottom. OB, Olfactory bulb;OP, olfactory placode; EYE, eye.Dashed lines indicate the outlines of the forebrain and the eyes. Scale bar, 60 μm. C–F, Axon pathfinding of developing olfactory sensory neurons in the right olfactory organ of living transgenic zebrafish embryos at 22 (C), 28 (D), 50 (E), and 72 (F) hpf. Dorsal is to the top, and medial is to the right. The anteroposterior axis is projecting out of the image. Arrows indicate the BPB, and asterisks indicate the nasal pit.OB, Olfactory bulb; OP, olfactory placode. Scale bar, 20 μm.
