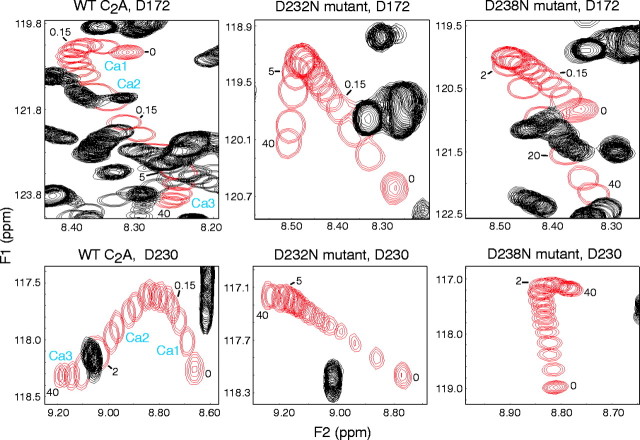
Fig. 1.
Intrinsic Ca2+ binding to the wild-type (WT) and the D232N and D238N mutant C2A domains of synaptotagmin 1 monitored by NMR spectroscopy. Ca2+ titrations were examined by1H-15N HSQC spectra acquired with 150–165 μm of purified recombinant C2A domains.Panels illustrate the Ca2+-dependent shifts of selected cross-peaks corresponding to the D172 (top panels) and D230 (bottom panels) NH groups in all three C2A domains. The cross-peaks from these NH groups are shown in red, and other cross-peaks are shown in black. Numbers next to the resonances indicate the Ca2+ concentration (in millimolar) for that particular position of the cross-peak. Note the typical triphasic movement of the cross-peaks in the wild-type C2A domain, with the corresponding Ca2+-binding sites (Ca1,Ca2, and Ca3) indicated next to each phase. In the mutants, only biphasic movements with a different Ca2+ dependence are detectable. For quantitation of the various Ca2+-binding parameters, see Table1.