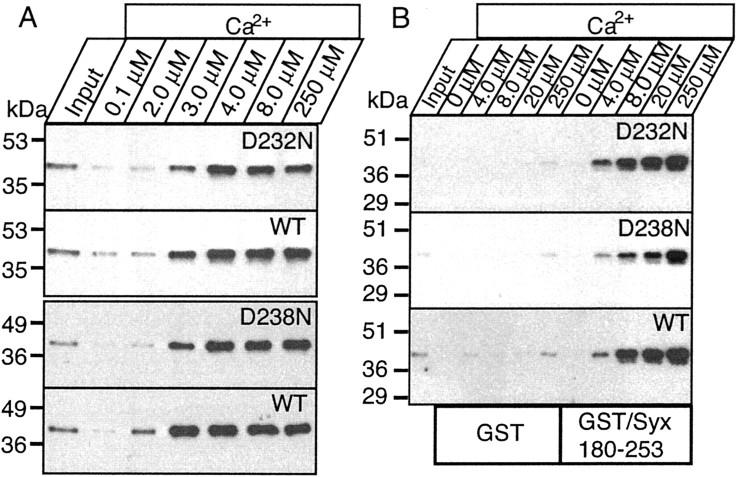
Fig. 7.
The D232N and D238N mutations do not cause a significant change in Ca2+-dependent phosphopholipid and syntaxin binding by native synaptotagmin 1. A, Soluble C2A/C2B domain fragments of native synaptotagmin 1 were obtained from wild-type and mutant littermate mice by partial trypsin digestion of brain membranes followed by centrifugation. The soluble C2A/C2B domain fragment released into the supernatant was used for binding experiments with liposomes at the indicated free Ca2+ concentrations. Input and bound proteins were then analyzed by immunoblotting using a monoclonal synaptotagmin 1 antibody. The two mutations were analyzed in independent experiments with their littermate wild-type controls, resulting in separate wild-type controls for each mutant. Numbers on theleft indicate positions of size markers.B, GST-pulldown experiments of the soluble C2A/C2B domain fragment of synaptotagmin 1 isolated as described above. Proteins were bound to GST and GST-syntaxin (residues 180–264) at the indicated concentrations of free Ca2+ as described in A, and bound proteins were visualized by immunoblotting.