Fig. 1.
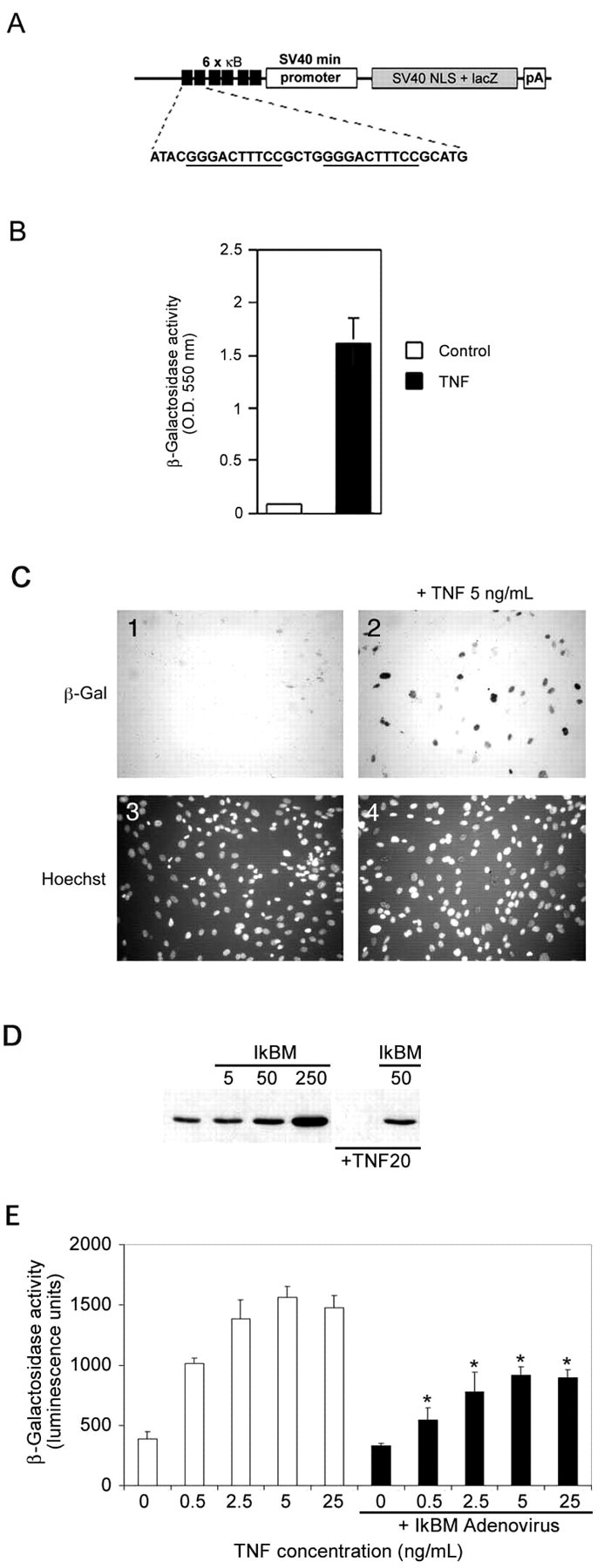
Transgene design and in vitrovalidation of the κB-dependent β-galactosidase construct.A, The NF-κB reporter minigene contains three tandem HIV-LTR repeats upstream of the SV40 minimal promoter, an E. coli β-galactosidase cDNA modified to contain a mammalian Kozak consensus, an SV40 T-antigen-derived nuclear localization signal, and a polyA tract derived from the protamine I gene. B, HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with the minigene and induced with DMEM + TNFα (5 ng/ml) or with DMEM alone (indicated as control) for 16 hr and analyzed for β-galactosidase activity.C, Primary MEFs derived from transgenic mice were incubated with (panels 2,4) or without (panels 1,3) TNFα (5 ng/ml) for 16 hr and then assessed for β-galactosidase activity. Cultures were counterstained with Hoechst 33342 (panels 3, 4) to show cell nuclei. D, MEFs were infected with 0, 5, 50, or 250 MOI of recombinant IκBαM adenovirus for 24 hr, and total cell lysates were prepared and analyzed by immunoblotting for IκBα. Wells that were mock infected or infected with 50 MOI of recombinant IκBαM adenovirus were exposed to TNFα (20 ng/ml) for 10 min. Endogenous IκBα is completely degraded by this treatment, but IκBαM is unaffected. E, Transgenic MEFs were incubated with 0, 0.5, 2.5, 5, and 25 ng/ml TNFα for 16 hr in the absence (whitebars) or presence (blackbars) of IκBαM adenovirus (∼50% infection efficiency). β-galactosidase activity was quantified using a chemiluminescent assay (Galacto-Star; Tropix). Each data point represents the average of six wells of a 24-well plate, and error bars indicate SD. Results were analyzed for statistical significance by ANOVA [Tukey honestly significant difference (HSD) multiple comparison], and statistically significant differences ofp < 0.001 are indicated by anasterisk.
