Fig. 5.
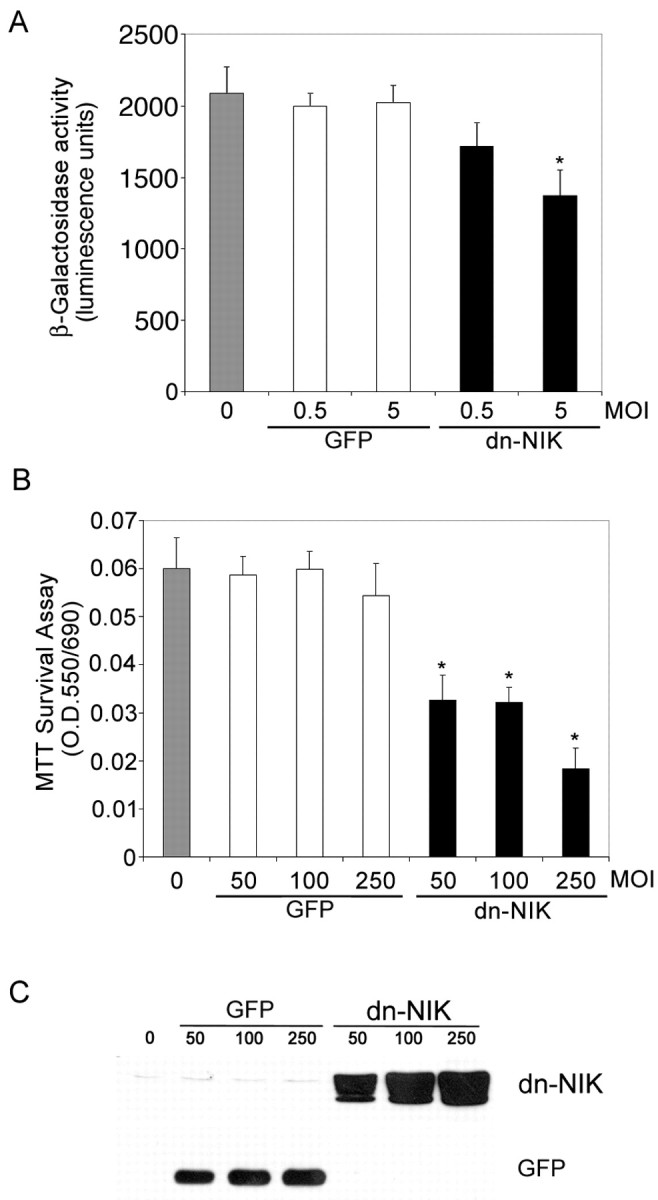
NIK signaling is required for NF-κB transcriptional activity and for neuronal viability in primary cortical neurons. A, E16 primary cortical neurons derived from a heterozygote litter were mock infected (gray bar) or infected with control GFP adenovirus (white bars) or dnNIK adenovirus (blackbars) at 0.5 or 5 MOI and harvested 4 d later. Lysates were analyzed for β-galactosidase activity using a chemoluminescence assay (Tropix). β-galactosidase activity was significantly reduced in cells infected with 5 MOI of dnNIK (*p < 0.03). B,C, Cortical neurons were infected with 0 (gray bar), 50, 100, or 250 MOI of recombinant adenovirus encoding GFP (white bars) or dnNIK (black bars) for 72 hr and then analyzed for viability by MTT dye conversion (B) and for GFP and dnNIK expression by immunoblotting (C). β-galactosidase overexpression had no significant effect on neuronal survival, but overexpression of dnNIK reduced survival at each MOI tested (*p < 0.001). A,B, Six wells were analyzed per condition, and results were analyzed for statistical significance by ANOVA (Tukey HSD multiple comparison). A–C, Each experiment was repeated at least three times.
