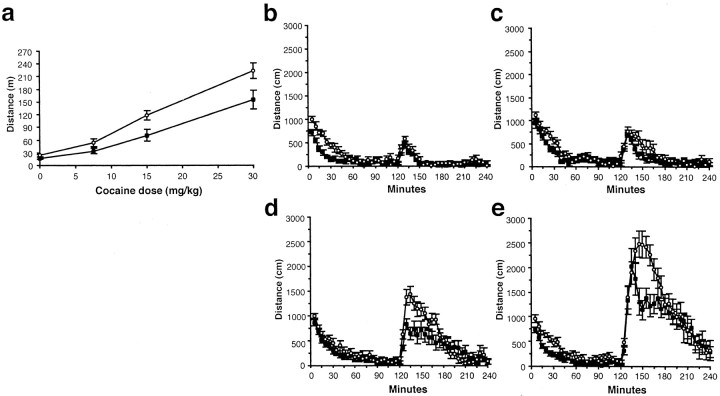
Fig. 2.
Effect of cocaine administration on locomotion.a, Distance traveled during the first hour after cocaine injection. A 2 × 4 ANOVA for dose and genotype revealed a significant effect of dose (F(3,117) = 67.3; p < 0.0001) and genotype (F(1,117) = 14.9; p< 0.001) but no interaction. Also shown is distance traveled during 5 min bins on day 4 with 0 (b), 7.5 (c), 15 (d), and 30 (e) mg/kg cocaine given by intraperitoneal injections at 120 min. The peak locomotion values for the 5-HT2C receptor mutants were significantly different from those of the WT mice (F(1,117) = 8.2; p= 0.005) and increased significantly with dose (F(3,117) = 85.7; p< 0.0001) without an interaction of dose and genotype.