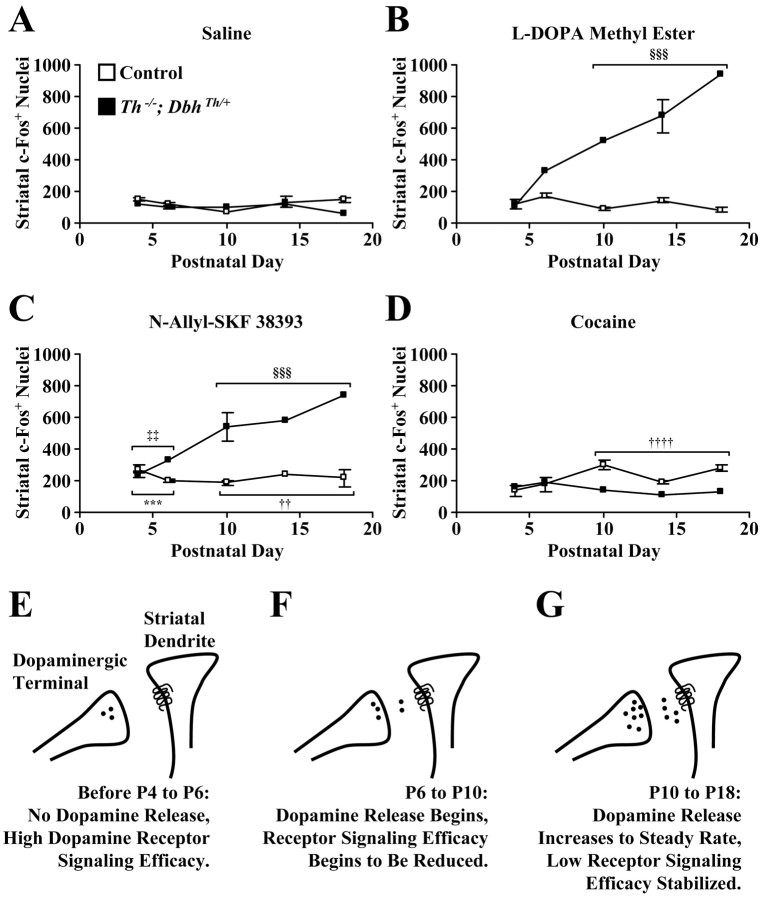
Fig. 5.
Quantitation of striatal c-Fos-positive nuclei 2 hr after treatments and a homeostatic model of dopamine receptor signaling efficacy during postnatal development. Values represent c-Fos-positive nuclei quantitated from images of entire striatal sections and are reported as means ± SEM at various postnatal stages. A, Values after saline treatment.B, Values after l-DOPA methyl ester (100 mg/kg) treatment. C, Values afterN-allyl-SKF 38393 (2.5 mg/kg) treatment.D, Values after cocaine (20 mg/kg) treatment. When mice at P4 and P6 and mice at P10, P14, and P18 were grouped together, three-way ANOVA revealed a significant interaction of phenotype, age, and drug (F = 20.99; df = 3, 121;p < 0.0001). Investigation of the causes of the complex interaction by two-way ANOVA revealed a significant interaction of age and drug for control mice (F = 9.24; df = 3, 92; p < 0.0001) and mutant mice (F = 7.25; df = 3, 29; p< 0.0001). ***p < 0.001, greater than saline response of pooled P4 and P6 control mice by one-tailed Dunnett's test. ††p < 0.01, ††††p< 0.0001, greater than saline response of pooled P10, P14, and P18 control mice by one-tailed Dunnett's test. ‡‡p< 0.01, greater than saline response of pooled P4 and P6Th−/−;DbhTh/+mice by one-tailed Dunnett's test. §§§p< 0.001, greater than saline response of pooled P10, P14, and P18Th−/−;DbhTh/+mice by one-tailed Dunnett's test. E, Before P4 and P6, midbrain dopaminergic terminals migrate into the striatum and produce dopamine, and some striatal neurons already express dopamine receptors. Dopamine receptor signaling efficacy is high. F, Between P6 and P10, presynaptic dopaminergic release and the propagation of signals in postsynaptic neurons begin. Dopamine signaling efficacy is reduced. G, From P10 to P18 and during adulthood, dopaminergic neurotransmission continues at a steady rate. Dopamine receptor signaling efficacy stabilizes at a low plateau.White squares, Control mice; black squares,Th−/−;DbhTh/+mice.