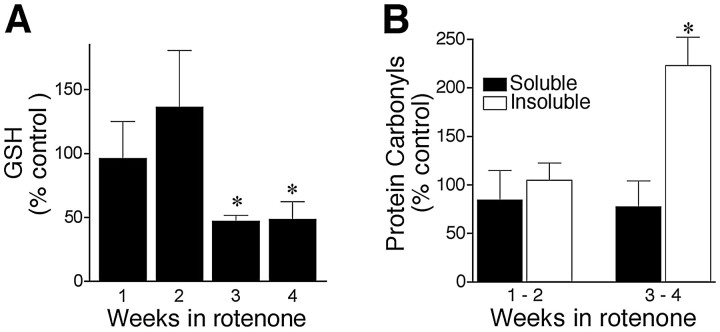
Fig. 3.
Chronic rotenone treatment caused delayed oxidative damage. A, Chronic rotenone exposure (5 nm) decreased cellular GSH. Control values at 1 week were 4.97 ± 1.2 nmol/mg of protein. Results are expressed as percentages of levels in control cells at each time point and represent mean ± SEM of four independent experiments at each time point.B, Delayed oxidative protein damage in rotenone-treated cells. Protein carbonyl levels are expressed as percentages of levels in control cells at each time point. Results show mean ± SEM of four independent experiments at each time point. *p< 0.05 compared with control.